Figure 1.
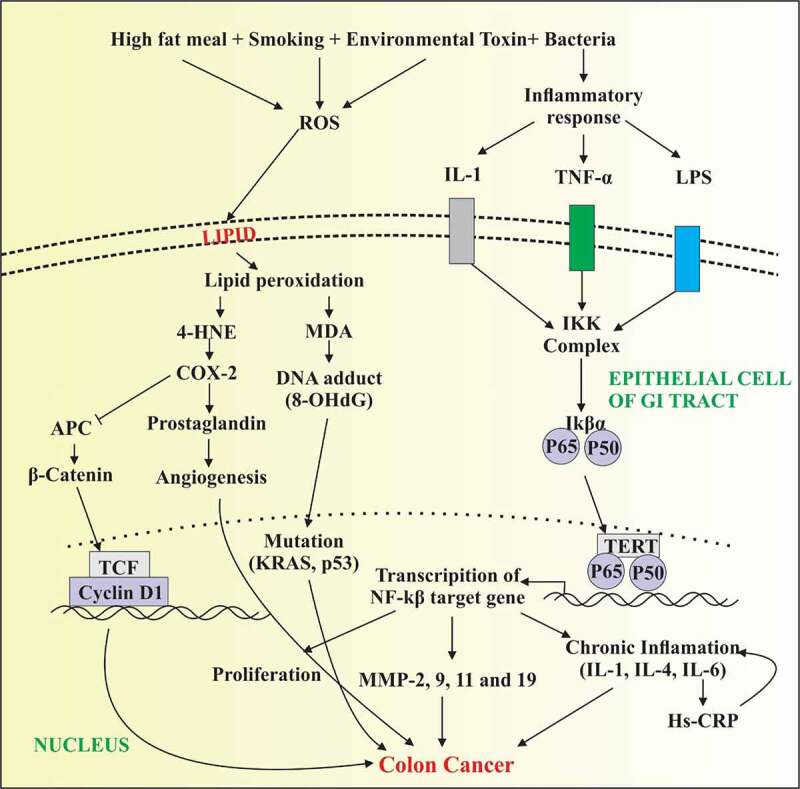
Depicting increased production of reactive oxygen species and inflammatory response that in turn trigger the activation of TNF-α, IL-1 and release of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) under external stimuli. Elevated level of free radicals cause damage to plasma membrane of epithelial cells of GI tract with increased formation of lipid peroxidation products. Further, 4-HNE activates COX2 production resulting in the activation of prostaglandin and B catenin that increase angiogenesis and proliferation of colon carcinomas. In parallel, LPS released from bacterial toxin and TNF- α cause the activation of NFkB signaling resulting in the transcription of NFkB target genes. Activation of several cytokines and MMPs cause increased proliferation of cancer cells resulting in tumor metastasis
