Figure 3.
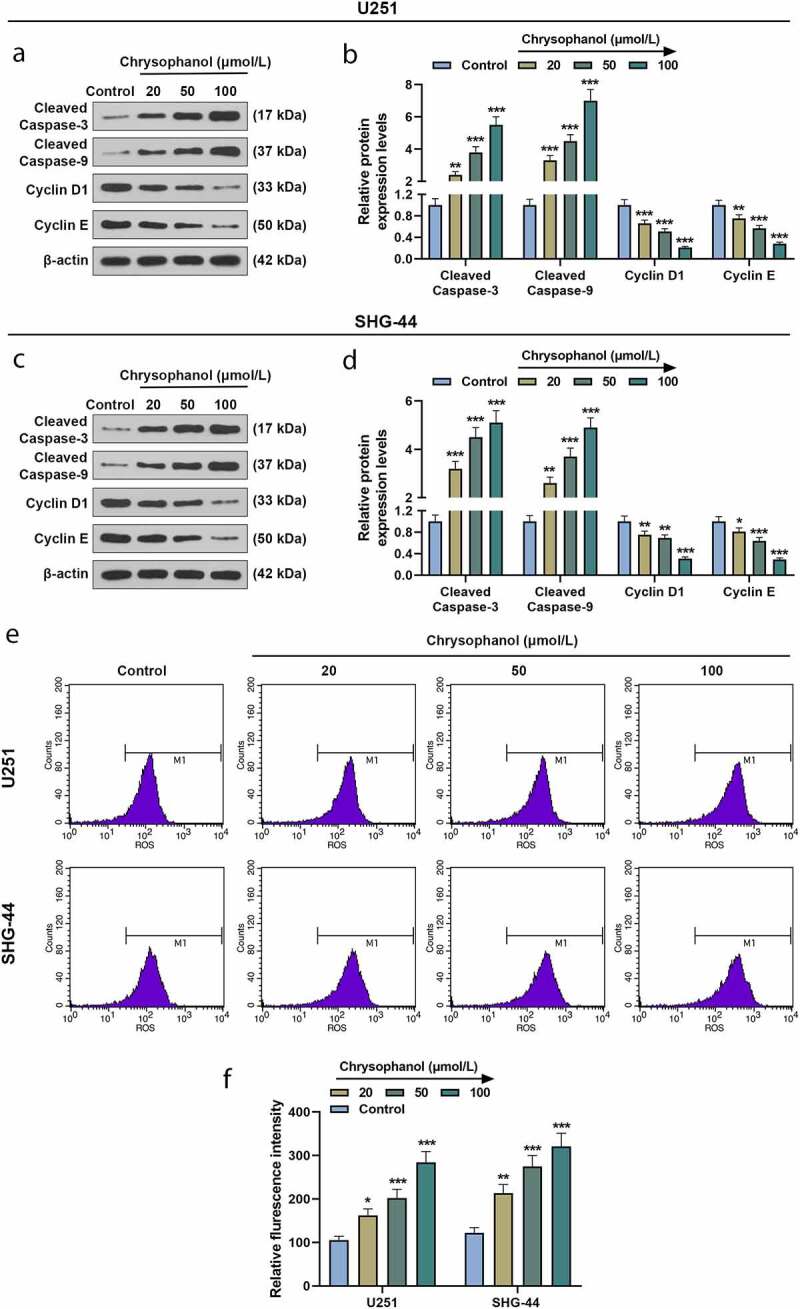
Chrysophanol increased cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 expressions as well as reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation while decreasing Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E levels in glioma cells. (a and b) Representative images of protein bands (a) as well as protein expression levels of Cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E in U251 cells were detected by western blot after treatment with different concentrations of chrysophanol. β-actin was used as a loading control. (c and d) Representative images of protein bands (c) as well as protein expression levels of Cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E in SHG-44 cells were detected by western blot after treatment with different concentrations of chrysophanol. β-actin was used as a loading control. (e) Representative images of ROS detection by flow cytometry after treatment with different concentrations of chrysophanol. (f) Flurescence intensity in U251 and SHG-44 was evaluated by flow cytometry after treatment with different concentrations of chrysophanol. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. Control group. All experiments were repeated independently at least three times. Data were expressed as the means ± standard deviation
