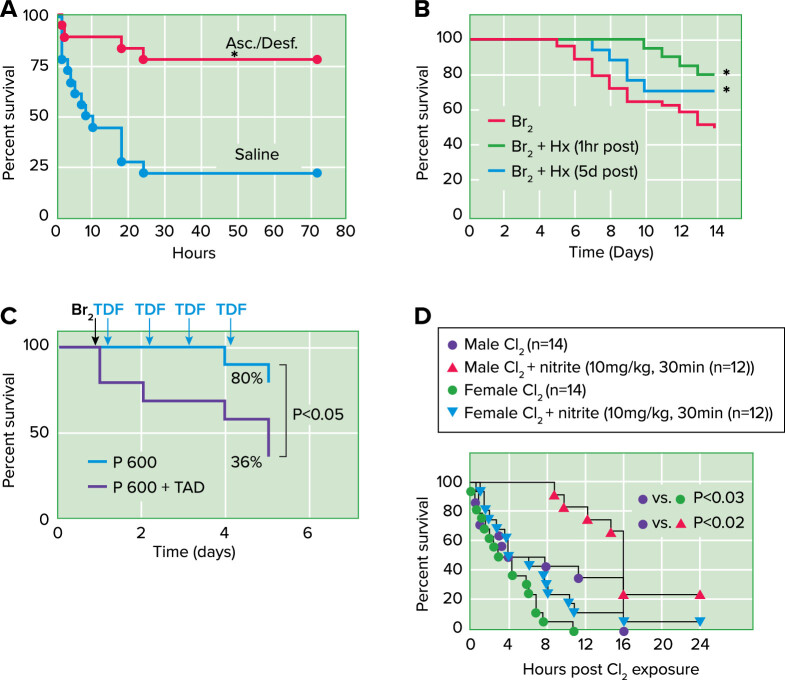
FIGURE 3.
Countermeasures against halogen toxicity. Post-Cl2 administration of antioxidants increase survival Mice were exposed to 600 ppm of Cl2 for 45 min and returned to room air. A: they received intramuscular injections of ascorbate (Asc; 2 mg) and deferoxamine (Desf; 0.3 mg) in saline starting at 1 h after exposure and every 12 h thereafter up to 60 h after exposure. They also received aerosols of ascorbate (150 mg/mL) and deferoxamine (0.3577 mg/mL) at 1.5, 24, and 48 h after exposure in sterile water. Control mice received vehicle (saline for intramuscular injections; sterile water for aerosols) instead of antioxidants using identical protocols. Data points were fitted with Kaplan-Meier survival curves and compared with the log-rank test (P = 0.0007) (from Ref. 41). B: post-Br2 exposure administration of hemopexin increases survival. C57BL/6 mice were exposed to Br2 (400 ppm for 30 min) and returned to room air. At either 1 h or 5 days post-exposure they were given a single intraperitoneal injection of purified human hemopexin (Hx) (4 µg/g body wt) or vehicle. Survival was assessed in the next 14 days. The Kaplan-Meier curve demonstrated that Hx reduced mortality after Br2 exposure, even when was given 5 days later. *P < 0.05 vs. Br2 + saline by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (68). C: post-Br2 administration of tadalafil (Cialis; TDF or TAD) decreases mortality of pregnant (P) mice. Nonpregnant (NP) and P gestational day 14.5 (E14.5) mice were exposed to air or to Br2 at 600 ppm for 30 min and returned to room air; they received tadalafil (TAD; 2 mg/kg body weight in 0.1 mL of sterile saline) or vehicle via oral gavage at 1 h post-exposure and every 24 h thereafter. Data show Kaplan-Meyer curves of P and NP mice with tadalafil or vehicle, post-Br2 exposure. NP mice exposed to Br2 and returned to room air lived longer than similarly exposed P mice (*P < 0.05) (from Ref. 55). D: post-Cl2 administration of nitrite improves survival. Male or female mice were exposed to Cl2 at 600 ppm, 45 min and then brought back to room air, and nitrite was administered by intramuscular injection 30 min post-exposure. Data show Kaplan-Meier survival curves. P < 0.03 between male and female Cl2-alone groups; P < 0.02 for nitrite therapy in males and P = 0.09 for nitrite therapy in females.