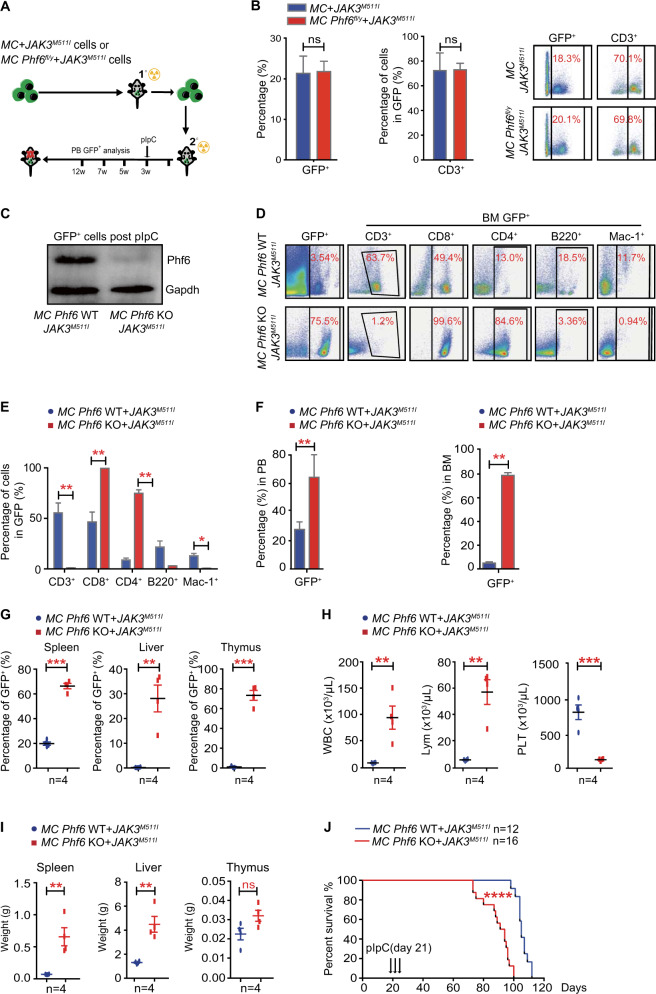
Fig. 3. PHF6 deficiency accelerates T-ALL development in the context of JAK3 mutation.
A Schematic representation of Phf6 deletion after JAK3M511I-induced T-ALL in a mouse model. B Left panel, percentage of GFP+ leukemia cells in the PB of mice at 3 weeks after transplantation. Right panel, percentage of CD3+ cells in GFP+ leukemia cells in the PB of mice at 3 weeks after transplantation. C The Phf6 protein expression level in GFP+ cells of T-ALL mice treated with pIpC. D, E Percentage of T cells, B cells and myeloid cells in GFP+ cells in the BM of T-ALL mice treated with pIpC. F Percentage of GFP+ cells in the PB and BM of T-ALL mice treated with pIpC. G Percentage of GFP+ cells in the spleen, liver, and thymus of T-ALL mice treated with pIpC. H The counts of WBCs, lymphocytes and platelets in the PB of T-ALL mice treated with pIpC by routine blood tests. I The weights of the spleen, liver, and thymus of T-ALL mice treated with pIpC. J Kaplan–Meier survival curves of MC Phf6 KO + JAK3M511I T-ALL mice (n = 16) and MC Phf6 WT + JAK3M511I T-ALL mice (n = 12) after pIpC injection (log-rank test P < 0.0001).