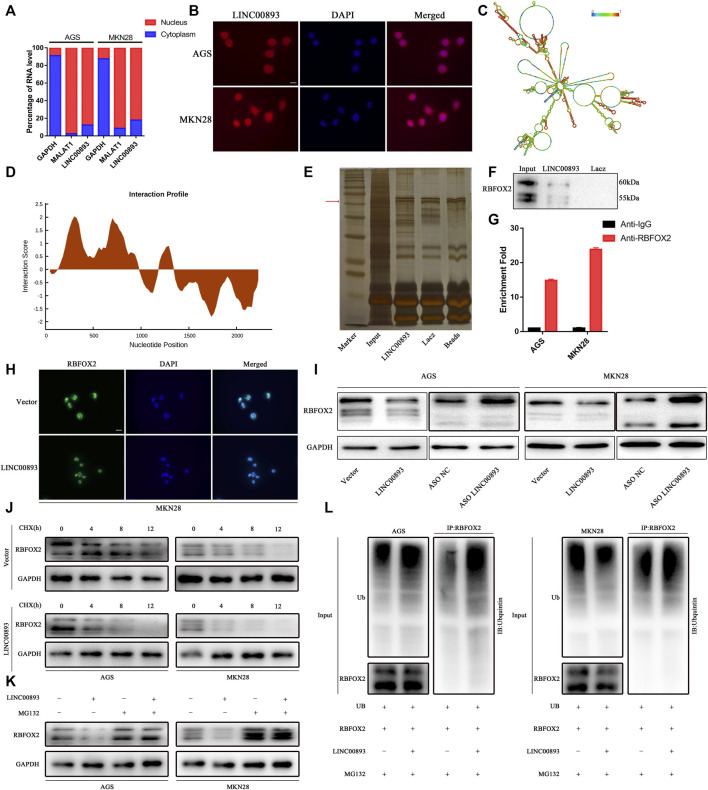
FIGURE 5.
Identification of RBFOX2 as a binding partner for LINC00893 (A) RT-qPCR analysis from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of GC cells; the cytoplasmic GAPDH mRNA and the nuclear lncRNA MALAT1 were used as controls (B) Subcellular localization of LINC00893 detected by FISH. Scale bar: 20 μm (C) The secondary structure of LINC00893 was predicted (http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at). The red color indicates strong confidence for the prediction of each base (D) The potential binding areas between LINC00893 and RBFOX2 were predicted using the catRAPID database (E) SDS-PAGE of proteins purified from CHIRP assay using biotinylated LINC00893 or antisense RNA (F) Western blotting analyses following CHIRP assays in AGS cells confirmed the interaction between LINC00893 and RBFOX2 (G) RIP assay followed by RT-qPCR suggested LINC00893 binds to RBFOX2 (H) Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for RBFOX2 expression in MKN28 cells after transfection with LINC00893 overexpression or empty vectors. Scale bar: 20 μm (I) Western blotting to analyze total level of RBFOX2 after LINC00893 were overexpressed or knocked down in GC cells (J) A CHX treatment was administered to assess RBFOX2 degradation in AGS and MKN28 cells (K) MG-132 abolished the downregulation of RBFOX2 protein expression induced by LINC00893 overexpression in AGS and MKN28 cells (L) Ubiquitination assays revealed that LINC00893 overexpression increased the level of the ubiquitinated RBFOX2 protein in AGS and MKN28 cells.