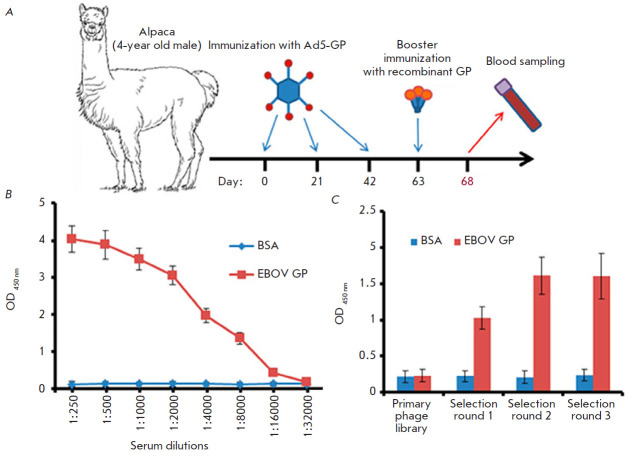
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of alpaca (Vicugna pacos) immunization to obtain a library of nanobodies (A), anti-EBOV GP antibody titers in the serum of immunized alpaca (B), and polyclonal phage ELISA (C). (B) – High-binding Polystyrene Microtiter plates were coated with 100 μl (1 μg/ml) of EBOV GP (H. sapiens-wt/GIN/2014/Kissidougou-C15). On the next day, the wells were washed with 0.1% PBST five times and blocked with 5% non-fat skim milk in PBST. Different dilutions of the serum in PBST were added, and the samples were incubated at 37°C for 1 h. The wells were washed five times, and Anti-Llama IgG Heavy- and Light-Chain antibodies (Bethyl, USA, A160-100P) in blocking buffer (1 : 5,000) were added for incubation at 37°C for 1 h. The wells were washed five times, TMB was added, and the results were evaluated. (C) – High-binding Polystyrene Microtiter Plates were coated with 100 μl of EBOV GP (H.sapiens-wt/GIN/2014/Kissidougou-C15). On the next day, the wells were washed with 0.1% PBST five times and then blocked with 5% non-fat skim milk in PBST. A total of 1011 phages from each stage of the selection were added in PBST and incubated at 37°C for 1 h. The wells were washed five times to remove unbound phages, and HRP-conjugated Anti-M13 antibodies (Abcam, UK, B62-FE2) in blocking buffer (1 : 5,000) were added for incubation at 37°C for 1 h. The wells were washed five times, TMB was added, and the results were evaluated