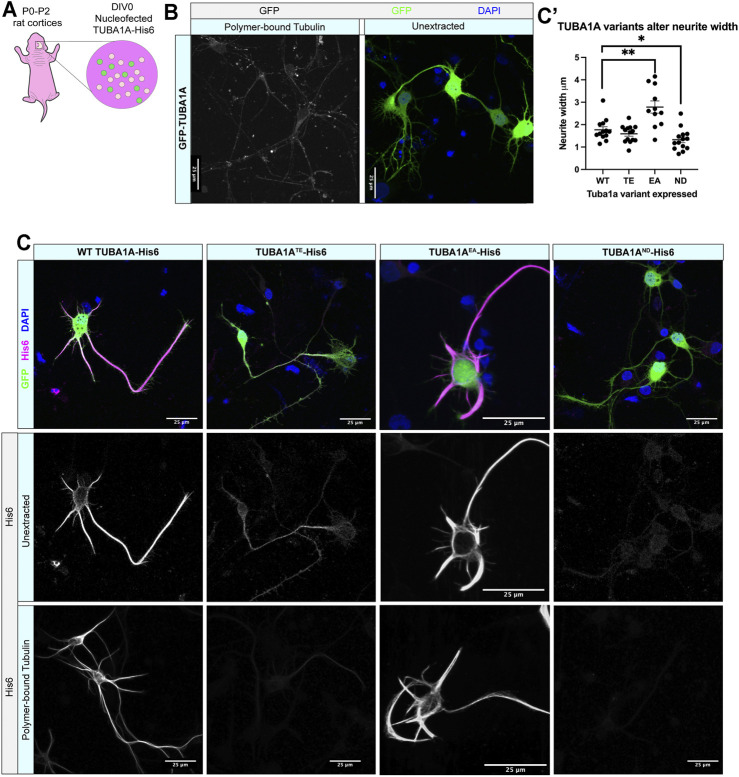
FIGURE 2.
TUBA1A ND α-tubulin does not incorporate into neuronal microtubule polymers. (A) Schematic of cortical neuron isolation and transfection. (B) Cortical rat neurons at DIV 2 transfected with TUBA1A-GFP. Left panel shows neurons with soluble tubulin dimers extracted, showing only GFP-labeled TUBA1A that is incorporated into microtubule polymer. Right panel shows neurons with intracellular environment intact (unextracted), containing soluble tubulin dimers and polymerized microtubules transfected to express a TUBA1A-GFP fusion protein. (C) Rat cortical neurons at DIV 2 transfected with wild-type (WT) TUBA1A-His6 (far left), TUBA1A TE -His6 polymerization-incompetent mutant as a negative control (middle left), TUBA1A EA stabilizing mutant as a positive control (middle right), TUBA1A ND -His6 (far right). Top panels show composite image containing membrane-bound GFP (green) for confirmation of transfection, α-His6 (Magenta) and DAPI (blue) immunolabeling. Middle panels show unextracted and bottom panels show different DIV2 neurons after tubulin has been extracted to reveal only polymer-bound tubulin, labeled with α-His6 antibodies to visualize ectopic TUBA1A-His6 proteins. Scale bar is 25 μm. (C′) A Scatter plot shows that neurons expressing His6-Tuba1aEA have significantly wider neurites than neurons expressing His6-Tuba1aWT and neurons expressing His6-Tuba1aND have neurites that are significantly thinner than neurons expressing His6-Tuba1aWT *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.