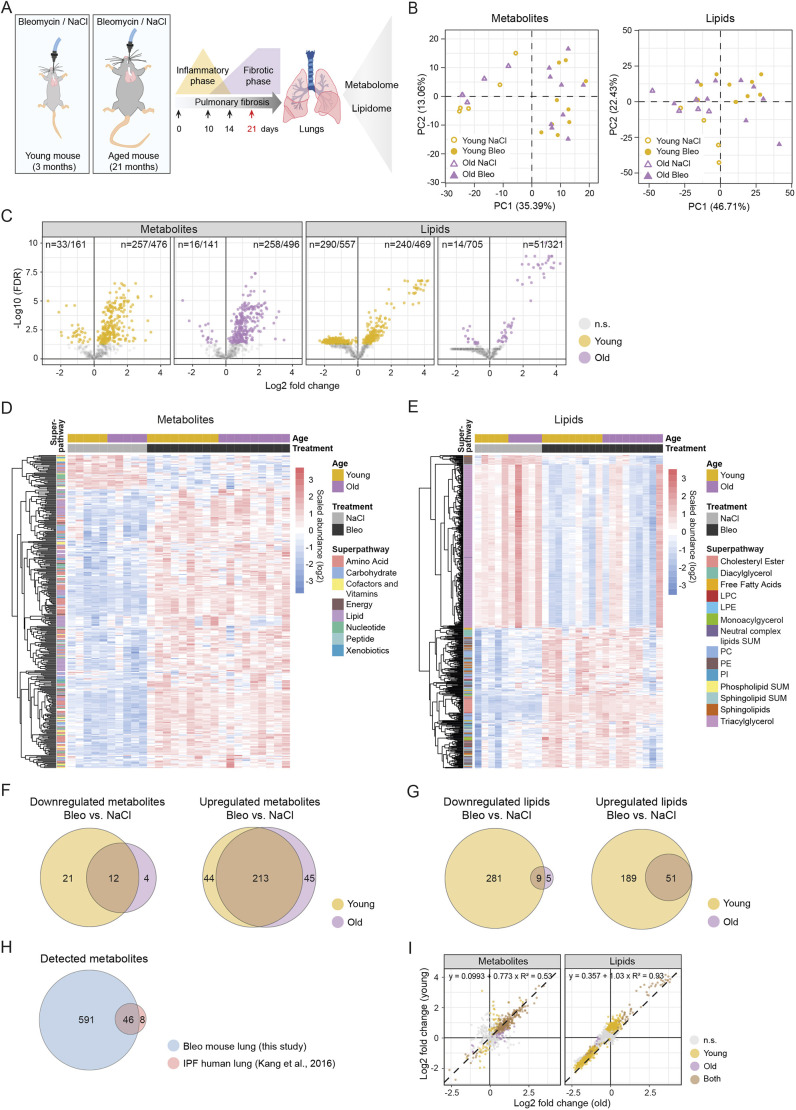
Fig. 1.
Detected and significantly deregulated metabolites and lipids in the lungs of young and old bleomycin-treated mice. (A) Schematic illustration of the study design. Young and old mice were instilled with bleomycin or saline solution (NaCl control), and the whole lungs were isolated on day 21 after treatment in the peak of the fibrotic phase. Metabolomic and lipidomic analyses were performed by mass spectrometry. (B) Principal component (PC) analysis of all lung samples, indicating separation between controls and bleomycin-treated animals, but not by age. (C) Volcano plots of all detected metabolites and lipids in young and old bleomycin-treated lungs. Significant entities are colored (one-way ANOVA), and the numbers for upregulated and downregulated metabolites and lipids are indicated. (D,E) Heat maps showing log2 scaled abundance of significantly deregulated metabolites (D) and lipids (E) in bleomycin-treated compared to control lungs in any age group. (F,G) Venn diagrams of significantly downregulated and upregulated metabolites (F) and lipids (G) of bleomycin-treated compared to control lungs in young and old mice. The metabolites and lipids that are significantly deregulated only in young, only in old or in both age groups are listed in Table S4. (H) Venn diagram of total detected metabolite numbers in this study in bleomycin-treated mouse lungs and in the published idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) study on human lungs compared to controls (Kang et al., 2016). (I) Scatter plots showing log2 fold changes of detected metabolites and lipids in young and old mice with their best linear fit (regression line, equation and coefficient of determination). FDR<0.05 in C-I. Bleo, bleomycin; FDR, false discovery rate; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; LPE, lysophosphatidylethanolamine; Neutral complex lipids SUM, total cholesteryl ester, monoacylglycerol, diacylglycerol, triacylglycerol, free fatty acid; n.s., not significant; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; Phospholipid SUM, total phosphatidylcholine, lysophosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylethanoamine, phosphatidylinositol; PI, phosphatidylinositol; Sphingolipid SUM, total sphingomyelin, ceramide, dihydroceramide, lactosylceramide, hexosylceramide.