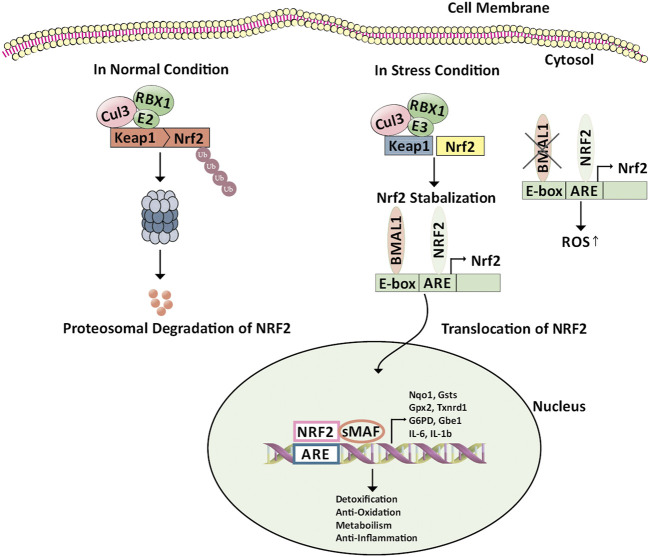
FIGURE 2.
Regulation of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway by BMAL1. Nrf2 is constitutively produced in the cell; however, in the absence of environmental stress, Nrf2 is sequestered in the cytoplasm by binding to an inhibitory protein, Keap1, which promotes continuous ubiquitinylation. Keap1 serves as a bridge between Nrf2 and the Cul3-Rbx1 E3 ubiquitin ligase. Cellular stress leads to modification of reactive cysteines within Keap1 that induces conformational changes resulting in Nrf2 stabilization. Here BMAL1 binds to the antioxidant response element through the E-box element present on the Nrf2 promoter leading to the transcription of Nrf2 and stabilization of the same. The NRF2 protein then translocates into the nucleus. There, it forms a heterodimer with other transcription regulators, such as small Maf proteins. The NRF2-sMaf complex binds to the ARE-containing genes in the nucleus involved in detoxification, anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation, and metabolism. The deficiency of BMAL1 disrupts the circadian rhythm of the Nrf2 pathway leading to cellular damage. Abbreviations: ARE, Antioxidant response element; BMAL1, Bone Muscle Arnt-like protein-1; Cul3-Rbx1 E3 ubiquitin ligase, Cullin 3-Ring box1 E3 ubiquitin ligase; E-box, Enhancer Box; G6pd, Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase; Gpx2, Glutathione Peroxidase 2; Gsts, Glutathione S-Transferase; IL-6, Interleukin-6; IL-1b, Interleukin 1 beta; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; NRF2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Nqo1, (NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1); sMaf, Small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; Txnrd1, Thioredoxin Reductase 1; Ub, Ubiquitin.