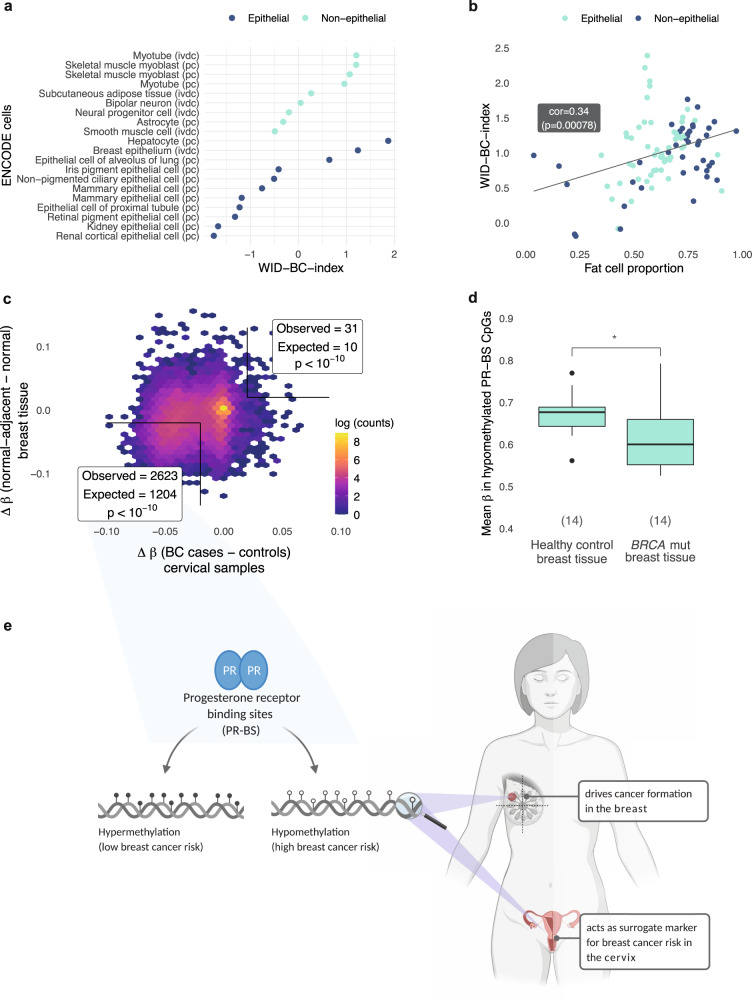
Fig. 6. Functional assessment of the WID-BC-index.
a The WID-BC-index evaluated in ENCODE primary cells (pc) and in vitro differentiated cells (ivdc). b The WID-index evaluated in ENCODE tissue samples. Correlation and p value assessed using Pearson’s correlation. c Difference in mean methylation (Δβ) at progesterone receptor binding site (PR-BS) CpGs between normal-adjacent and normal tissue in breast samples versus the Δβ in breast cancer cases and controls in cervical samples. CpGs with Δβ > 0.02 or Δβ < 0.02 were considered hypo- or hyper-methylated respectively. Observed/expected values and p values were assessed using Chi-Squared test: hypomethylated CpGs: p < 2.2e-16; hypermethylated CpGs: p = 1.349e-11. d Mean methylation of the 2,623 hypomethylated PR-BS CpGs in normal breast samples from healthy controls and women with BRCA mutation (*p = 0.019 in two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Values in brackets indicate sample numbers (n = 14 healthy controls, 14 BRCA mutation carriers). Box plots correspond to standard Tukey representation, with boxes indicating mean and interquartile range, and lines indicating smallest and largest values within 1.5 times of the 25th and 75th percentile, respectively. Dots indicate outlier values. e Schematic illustration created using Biorender. Hypomethylation at PR-BS CpGs is associated with an increased breast cancer risk and can be detected in breast tissue at risk and in cervical samples. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.