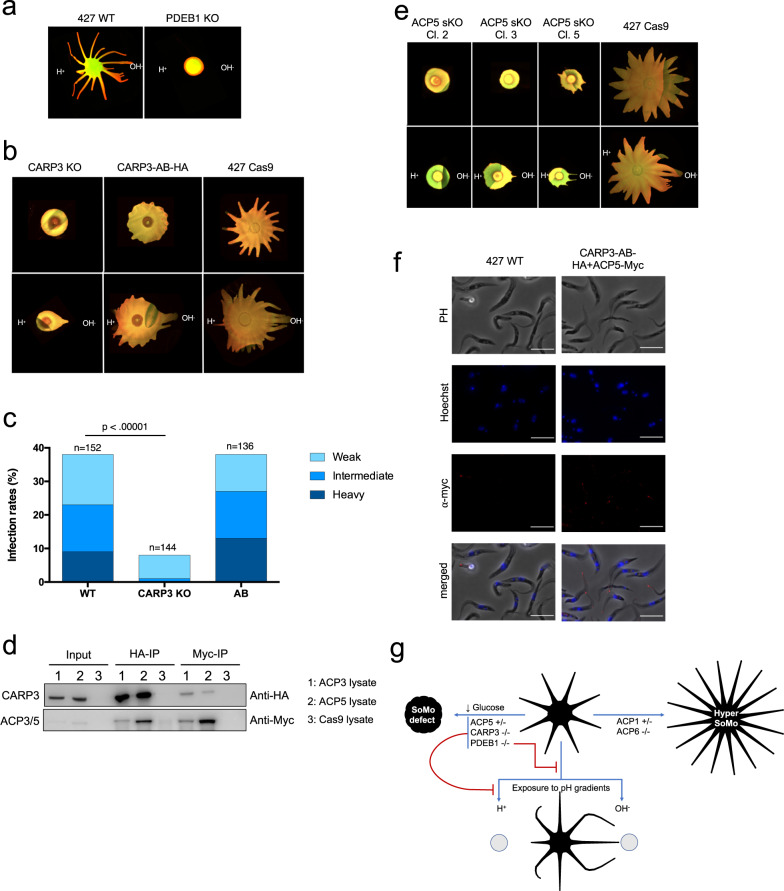
Fig. 6. CARP3 is required for acid sensing in vitro and for establishment of infection in flies.
a Merged EP and GPEET signals of Lister 427 wt and PDEB1 knockout (KO). b Merged EP and GPEET signals of 427 Cas9 parental line, CARP3 knockout and CARP3-HA addback. Upper panel: untreated. Lower panel: exposed to acid and alkali. c Teneral flies were infected with wild-type Lister 427 procyclic forms (WT), the CARP3 double knockout (CARP3-KO) and the addback (AB). Dissections were performed 13–14 days post infection. Total numbers are derived from two replicates per cell line (Supplementary Table 2). The intensity of midgut infections was scored as heavy, intermediate or weak as described36. The p-value is shown for Fisher’s exact test, two-sided (p-value = 2.0117−10). d Western blot analysis of immunoprecipitations with anti-HA and anti-myc antibodies (representative blot from three independent experiments). Myc-tagged ACP3 and ACP5 were expressed independently in the CARP3-HA background. The parental line 427 Cas9 was used as a control. Input samples have 40 times fewer cell equivalents than the immunoprecipitated samples. IP: immunoprecipitation with anti-HA or anti-myc antibodies. e Merged EP and GPEET signals of the 427 Cas9 parental line and 3 independent ACP5 single allele knockouts; panels as in (b). f Myc-tagged ACP5 is localised to the flagellar tip in a cell line co-expressing CARP3-HA. Immunofluorescence was performed with an anti-myc antibody (red). DNA was stained with Hoechst dye. Scale bar = 10 µm. g Summary of mutants, SoMo phenotypes and responses to pH. −/−: double knockouts; +/−: single knockouts. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.