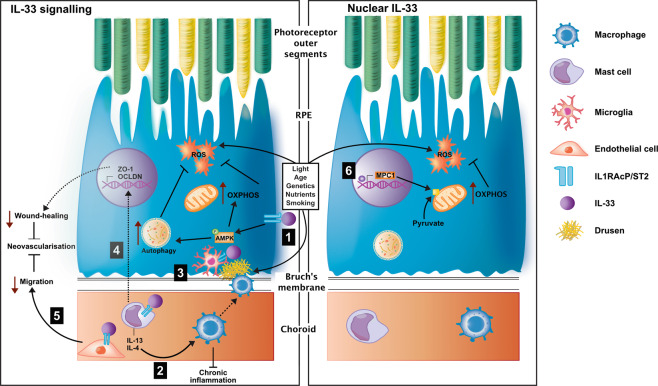
Fig. 3. IL-33 therapeutic potential in early AMD.
The interleukin-33 biological function has The potential to protect against early pathogenic pathways in AMD via dual function, as a signalling molecule and nuclear factor. With diverse cellular targets, IL-33 can stimulate 1) retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) in the eye directly, increasing AMPK phosphorylation and subsequent mitochondrial metabolism78. AMPK phosphorylation can also increase autophagy. Both will combat reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and oxidative stress. 2) IL-33 influences alternative activation of macrophages by stimulation of mast cells to release IL-13 and IL-468, which can promote inflammation resolution. 3) IL-33 stimulation of an alternative microglia phenotype promotes deposit clearance in Alzheimer’s disease models59,73 and could prove beneficial against drusen. 4) IL-33 stimulated mast cells to induce changes to tight-junction proteins in RPE cells 5) and directly stimulate retinal endothelial cells reducing migration71, both important in mediating wound-healing responses. 6) Nuclear IL-33 is a key metabolic regulator in RPE cells, promoting increased mitochondrial metabolism (OXPHOS; oxidative phosphorylation)78. The dashed line indicates indirect evidence.