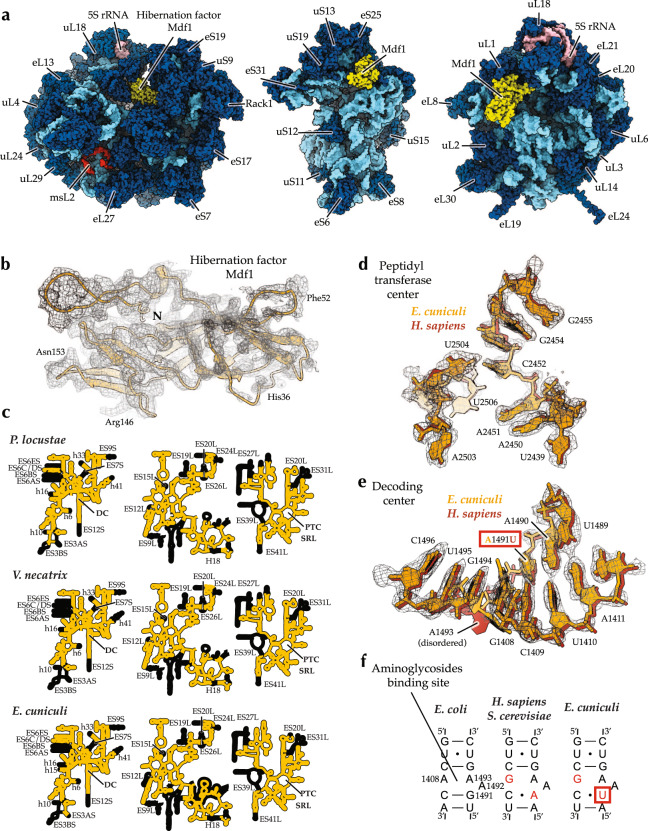
Fig. 1. Electron microscopy reveals the structure of the miniaturized ribosomes from the human pathogen Encephalitozoon cuniculi.
a The structure of E. cuniculi ribosomes in complex with the hibernation factor Mdf1 (pdb id 7QEP). b The map of the hibernation factor Mdf1 bound to E. cuniculi ribosomes. c Secondary structure diagrams compare rRNA reduction in microsporidian species with known ribosome structures. The panels indicate the location of rRNA expansion segments (ES) and ribosomal active centers, including the decoding site (DC), the sarcin-ricin loop (SRL), and the peptidyl-transferase center (PTC). d The electron density corresponding to the peptidyl-transferase center of E. cuniculi ribosomes shows that this catalytic site has the same structure in the parasite E. cuniculi and its hosts, including H. sapiens. e, f The electron density corresponding to the decoding center (e) and schematic structures of the decoding center (f) illustrate that E. cuniculi have U1491 residue instead of A1491 (E. coli numbering) in many other eukaryotes. This variation suggests that E. cuniculi may have sensitivity to the antibiotics targeting this active site.