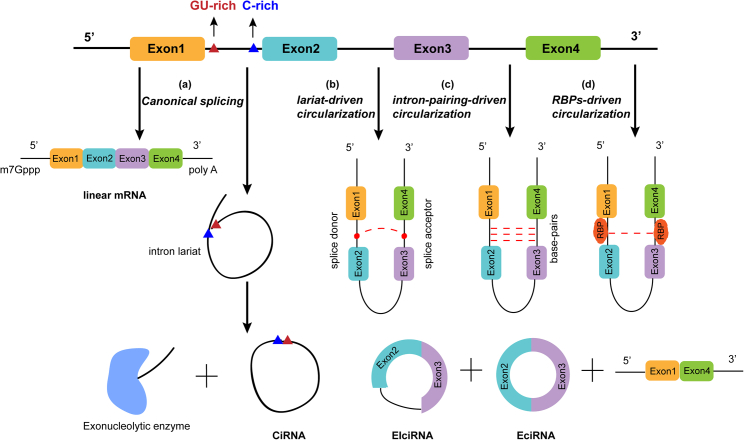
Figure 2.
The models of circRNAs biogenesis
(A) Canonical splicing: The GU-rich element near the 5′ splice site and C-rich element close to the branchpoint site were ligated to form ciRNAs. (B) Lariat-driven circularization: The 5′ splice donor site of exon 4 covalently binds to the 3′ splice acceptor site of exon 1 to form lariat structure and produce EIciRNAs or EciRNAs. (C) Intron-pairing-driven circularization: The complementary base pairs between introns bring splicing sites close to form EIciRNAs or EciRNAs. (D) RBP-driven circularization: RBPs bridge distal splice site to facilitate cyclization.