Fig. 5.
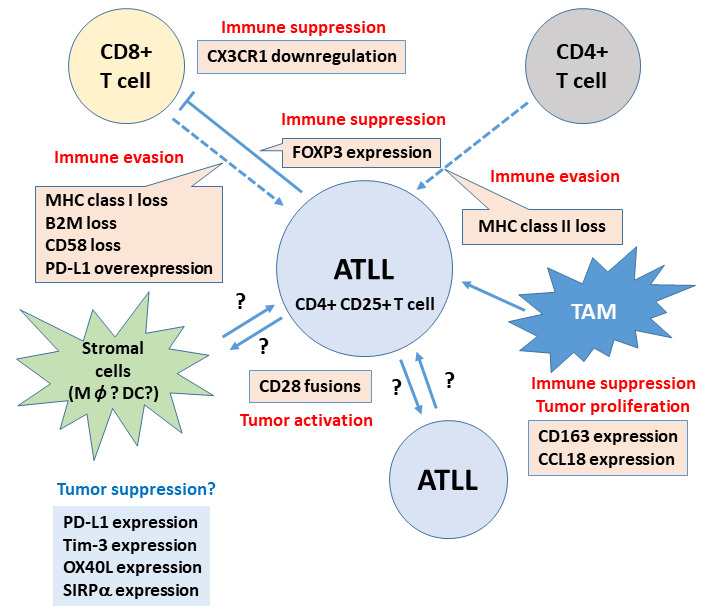
The microenvironment of ATLL. Scheme summarizing recent findings of the tumor microenvironment of ATLL. Immune evasion from CD8+ T-cells by loss of MHC class I and class II, loss of CD58, and overexpression of PD-L1 has been reported. Loss of MHC class II may be important for immune evasion from CD4+ T-cells. Immune suppression by TAMs, chemokines, and Treg function of ATLL itself was also reported. Interaction between CD80/CD86 and CD28 fusion proteins can mediate continuous CD28-mediated tumor activation. However, some stromal cells express immune checkpoint molecules and/or SIRPα, which play a role in the better prognosis of ATLL patients through an unknown mechanism.
ATLL, adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand-1; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; Treg, regulatory T-cell; SIRPα, signal-regulatory protein alpha
