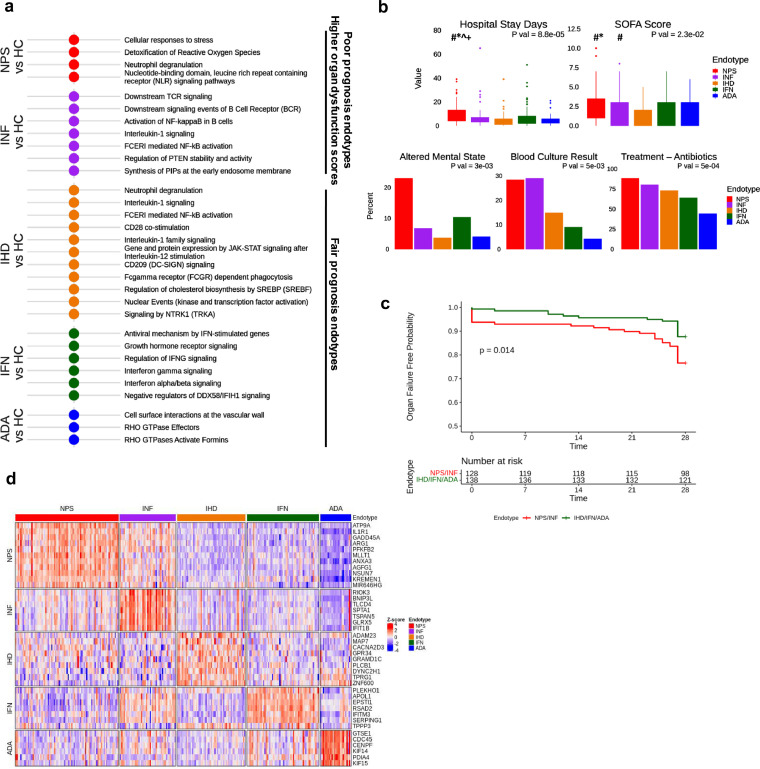
Figure 2.
Biological and clinical characterization of Neutrophilic-Suppressive (NPS), Inflammatory (INF), Innate-Host-Defence (IHD), Interferon (IFN), and Adaptive ADA) endotypes and their respective signatures. (a) Functional enrichment of up and downregulated DE genes (displaying ≥ ±1.5-fold change; adjusted p ≤ 0.05) comparing each endotype to healthy controls (n = 39). (b) Selected clinical symptomology and outcomes of endotypes and their distributions. Dunn's Posthoc test indicated by: # p < 0·05 cf. IHD; * p < 0·05 cf. IFN; + p < 0·05 cf. ADA; ^ p < 0·05 cf. INF. (c) Kaplan-Meier curves describing 28-day organ failure free days. Organ failure free days was compared between endotypes by combining the low prognosis endotypes (NPS and INF) and the fair prognosis endotypes (IFN, IHD, and ADA). The combined endotypes shared many molecular and clinical features, so this scheme made biological sense and increased statistical power to detect a significant difference. (d) Heat map showing the expression of 40 classification genes (used to drive the endotype classification model) in all patients (arrayed left to right). NB this signature delivered excellent performance in the discovery group (AUC/accuracy: 96%; Sensitivity: 81%; Specificity: 95%).