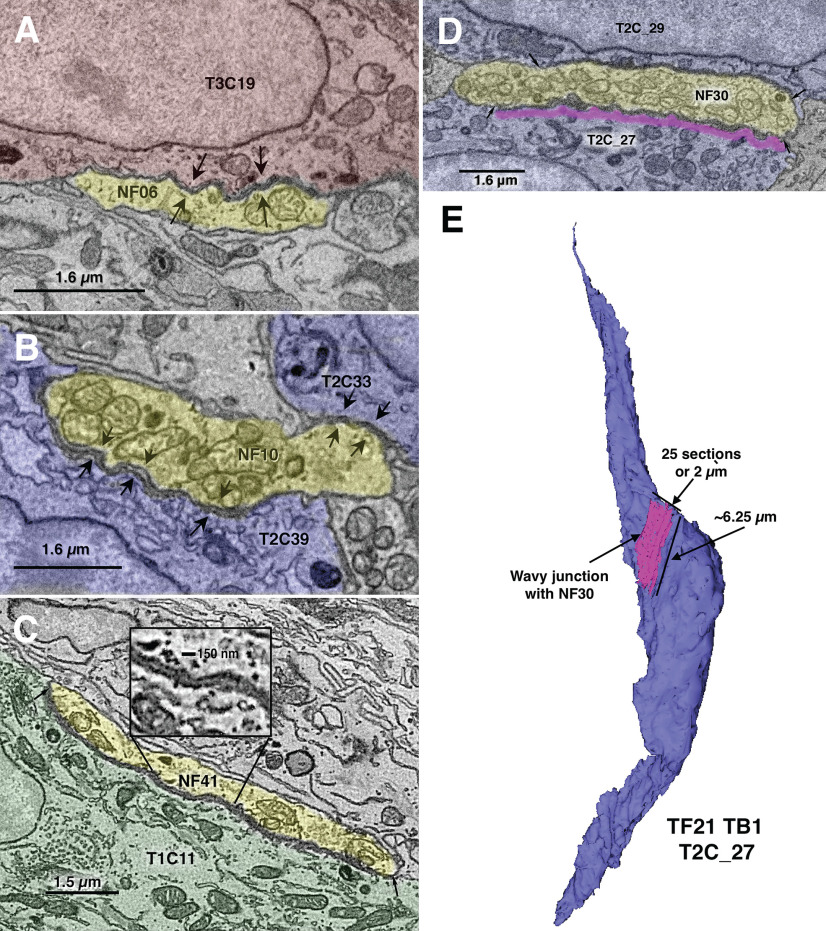
Figure 2.
Examples of wavy junctions between NFs (yellow) and diverse cells of taste buds. A, From TF21_TB2: wavy junction between a NF (NF06, yellow) and a Type III cell (T3C19, red). Arrows mark the extent of the contact, in this case ∼3 μm. B, From TF21_TB1: wavy junction between a NF (NF10, yellow) and two Type II cells, T2C39 and T2C33, blue. Arrows mark the extent of the contacts, in this case ∼1 μm for T2C33 and ∼3.5 μm for T2C39. C, From DS2_TB3: wavy junction between a NF (NF41, yellow) and a Type I cell (T1C11, green). The inset shows an enlargement of the gap region of ∼40–50 nm. Arrows mark the extent of the contact, in this case ∼8 μm. D, A large wavy junction from TF21_TB1 cell T2C27. Magenta shows the extent of the wavy junction with NF30. E, Reconstruction of cell T2C27 and its wavy junction with NF30 corresponding to the single plane image in D.