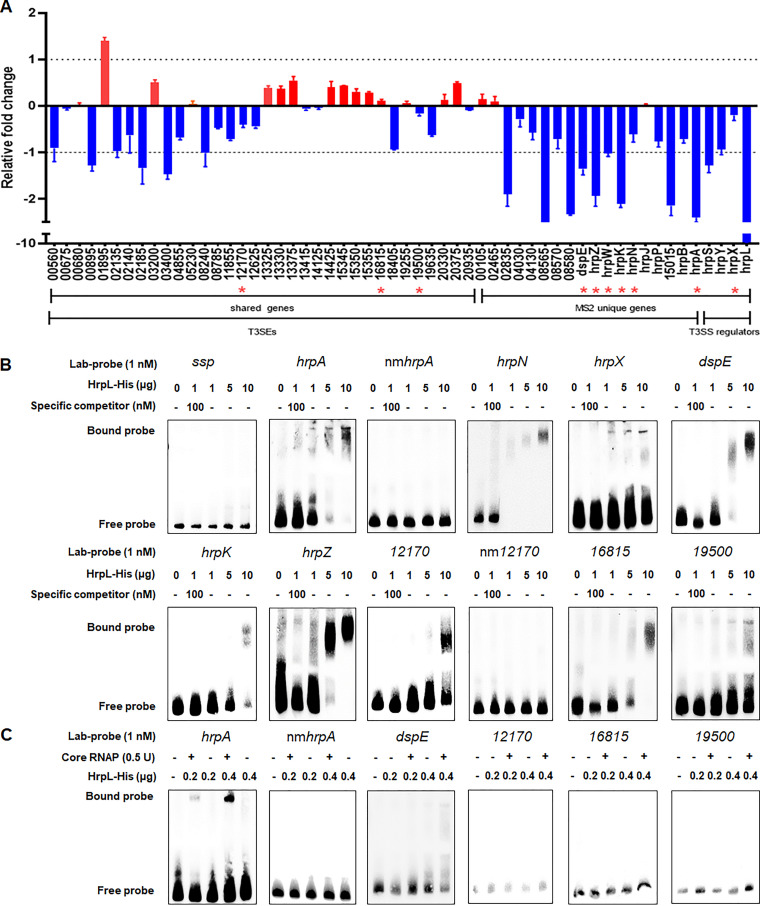
FIG 8.
The T3SEs regulated by the HrpL regulator. (A) qRT-PCR of the predicted T3SEs in the genome of MS2. The expression of the predicted T3SE encoding genes (listed in Table 2), including 34 genes shared in both MS2 and JZL7 genomes and 15 genes present uniquely in the MS2 genome, as well as the regulatory genes hrpX, hrpY, hrpS, and hrpL, were measured by qRT-PCR. Expression of the housekeeping gene atpD was used as a reference. The y axis indicates the values log2(fold change of ΔhrpL mutant relative to wild-type MS2). Red bar indicates expression levels higher in the mutant, while blue indicates those lower in the mutant. Red stars indicate the target genes whose promoters were verified to be interacted by HrpL protein in the panel below. (B) EMSA of the T3SEs with predicted hrp box. The promoter DNA fragments of the genes C1O30_RS12170, C1O30_RS16815, C1O30_RS19500, dspE, hrpZ, hrpK, and hrpN and the known HrpL-regulated gene hrpA, which contain the predicted hrp box in Table 2, were amplified and labeled by biotin and then performed for EMSA with different concentrations of the expressed and purified HrpL protein. Fragments without hrp box (non GGAACC-Nx-CCACNNA motif) in the hrpA and C1O30_RS12170 promoters, designated nmhrpA and nm12170, respectively, were amplified and used for EMSA reaction to confirm the importance of the presence of hrp box. For specific competition, a 100 nM unlabeled DNA fragment was incubated with 1 μg HrpL protein for 15 min before addition of a 25 nM labeled DNA fragments. (C) E. coli core RNAP (0.5 U) was incubated on ice for 20 min with 0.2 or 0.4 μg of purified HrpL protein. The remaining steps were as described above.