Fig. 1. Ultrastructure of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) accessible in clinical imaging.
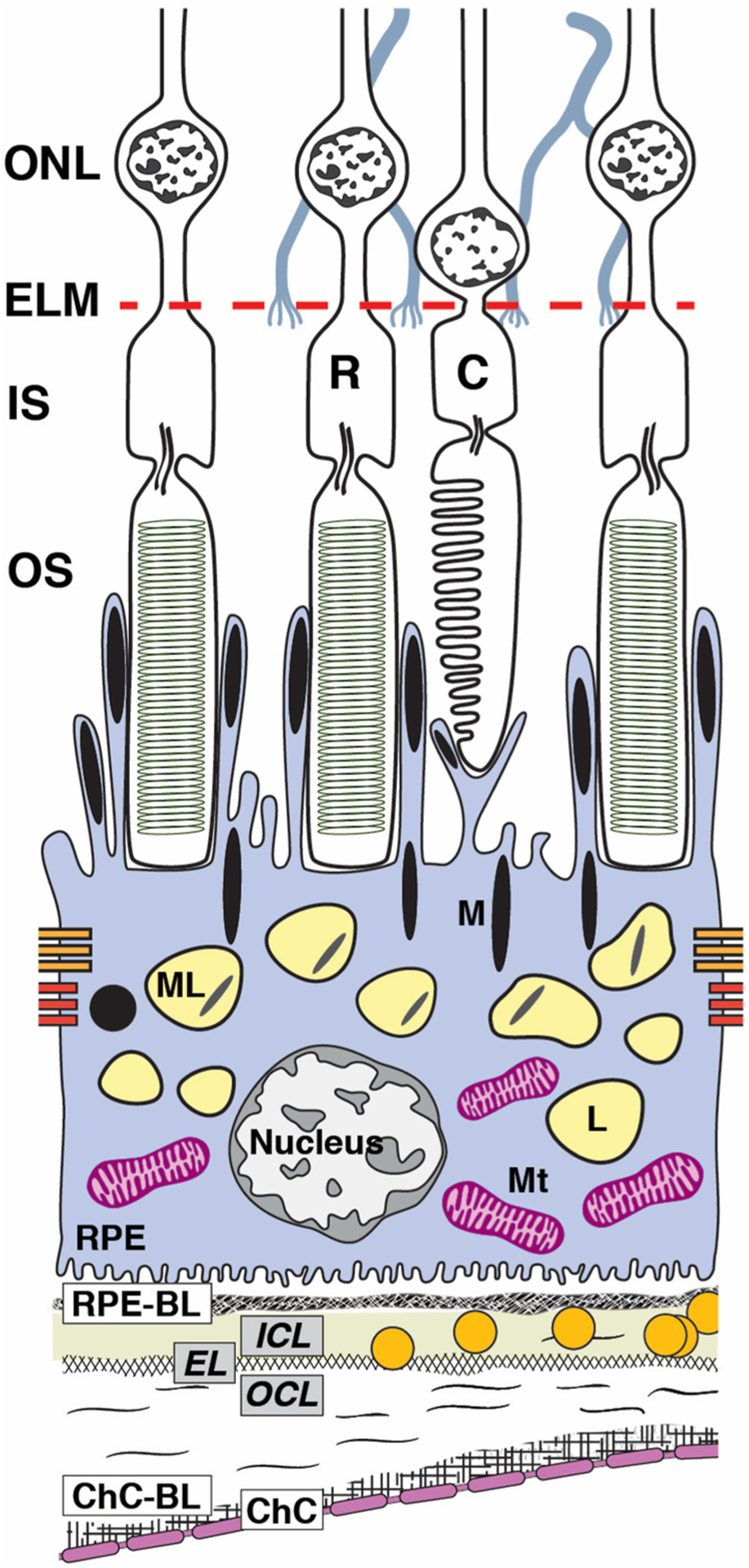
The RPE, as an epithelium, rests on a basal lamina (BL) of specialized extracellular matrix as it serves photoreceptors above and choroidal vasculature below. RPE cell bodies contaiñ1400 organelles of imaging significance in two cushions of similar numerosity (Bermond et al., 2020; Pollreisz et al., 2018, 2020): lipofuscin (L) and melanolipofuscin (ML) with some melanosomes(M) in the apical ¾, mitochondria (Mt) in the basolateral ¾, with the middle ½ containing both organelle classes. Apical processes are thin (0.3 μm in cross--section) and at least 15 μm long. Some surround rod outer segment tips at the cell body surface. Others extend upward to surround the shorter outer segment tips of cones. RPE-specific melanosomes are spindle-shaped (elongated), with ~2/3 in the apical processes and 1/3 at the apical aspect of the cell body, many standing upright. Spherical non-autofluorescent electron-dense organelles may represent a second population of melanosomes. In consensus nomenclature for spectral domain OCT (Staurenghi et al., 2014), 4th reflective band components include RPE cell bodies, basal infoldings, RPE-BL, basal laminar deposit and/or contents of sub-RPE-BL space if present, and ICL-EL-OCL of BrM. The 3rd outer retinal hyperreflective band of OCT, called interdigitation zone (IZ), corresponds to interleaved outer segments and RPE apical processes with their organelles. For illustrative clarity, drawing and proportions of specific organelles are not to scale. C, cone; ChC, choriocapillaris; ChC-BL, ChC basal lamina; EL, Elastic layer; ELM, external limiting membrane; ICL, inner collagen layer; IS, inner segments of photoreceptor; M, melanosome; ML, melanolipofuscin; Mt, mitochondria; OCL, outer collagen layer; OS, outer segments of photoreceptors; R, rod; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; RPE-BL, RPE basal lamina.
