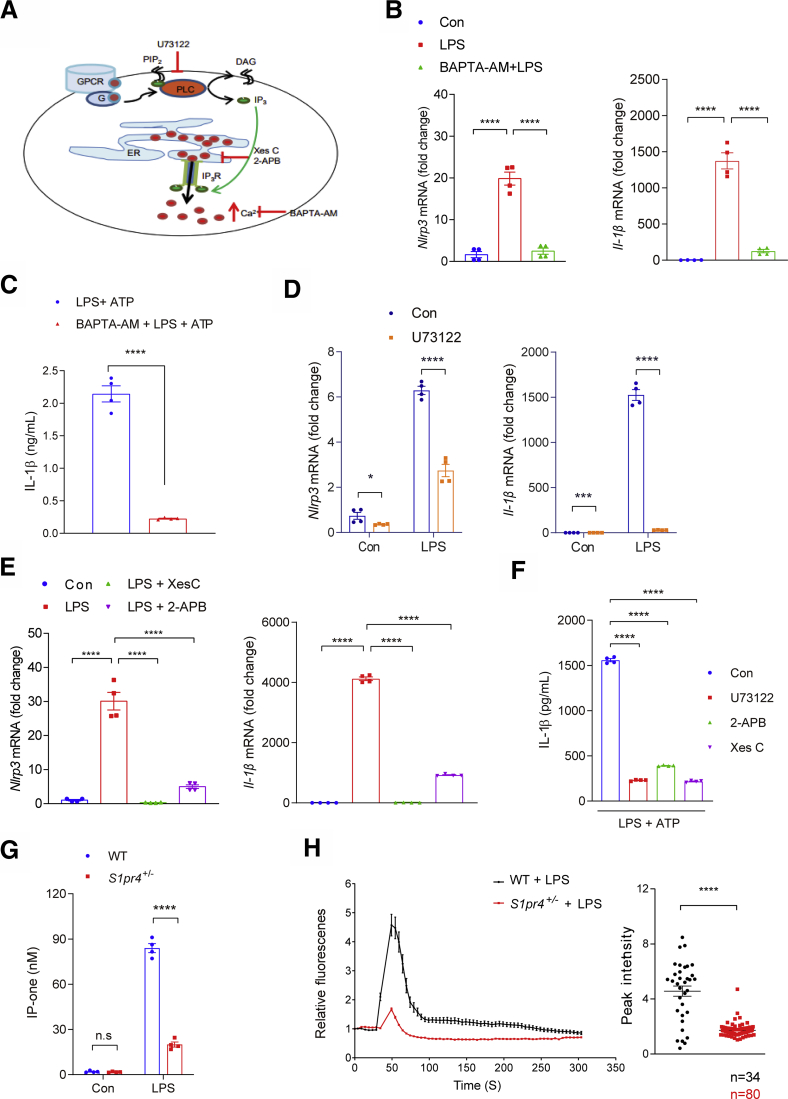
Figure 5.
Intracellular calcium signaling is necessary for S1PR4-dependent activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatic macrophages. (A) Schematic illustration of inhibitor of PLC and IP3. (B and C) Effect of calcium depletion on LPS-induced activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Relative mRNA expression levels of (B) Nlrp3 and Il-1β in the cells and (C) IL-1β secretion into the culture medium (n = 4). (B) Hepatic macrophages were pretreated with BAPTA-AM (10 μmol/L) for 30 minutes and then treated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 3 hours. (C) In another set of experiments, LPS-primed hepatic macrophages were treated with ATP (1 mmol/L) for 30 minutes. (D–F) Inhibition of LPS-induced NLRP3 inflammasome pathway by suppression of the PLC/IP3/IP3R axis. (D) Relative mRNA expression levels of Nlrp3 and Il-1β. Hepatic macrophages were treated with (D) 10 μmol/L U73122, (E) 5 μmol/L Xes C or 100 μmol/L 2-APB (n = 4). (F) IL-1β in the culture medium. Hepatic macrophages pretreated with U73122 (10 μmol/L), Xes C (5 μmol/L), or 2-APB (100 μmol/L) for 30 minutes and dimethyl sulfoxide as vehicle control. Hepatic macrophages were treated with 1 mmol/L ATP for 30 minutes after 3 hours of LPS priming (100 ng/mL). IL-1β secreted in the culture supernatants was quantified by ELISA (n = 4). (G and H) S1PR4-dependent calcium release from ER plays a pivotal role in the priming of NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatic macrophages. (G) Levels of IP-one in S1pr4+/- hepatic macrophages (n = 4). (H) Effect of S1PR4 on LPS-mediated [Ca++] release. WT or S1pr4+/- hepatic macrophages were incubated with Fluo-4/AM followed by stimulation with LPS for 2 hours. [Ca++] was analyzed by time-lapse confocal microscopy (left panel). Quantification of LPS-induced peak fluorescent intensities (right panel). All data are shown as means ± SEM. (C, D, G, and H) Data were analyzed by Student two-tailed unpaired t test. (B, E, and F) Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction. ∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .001, and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. Con, control; DAG, diacylglycerol; G, G-protein; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor.