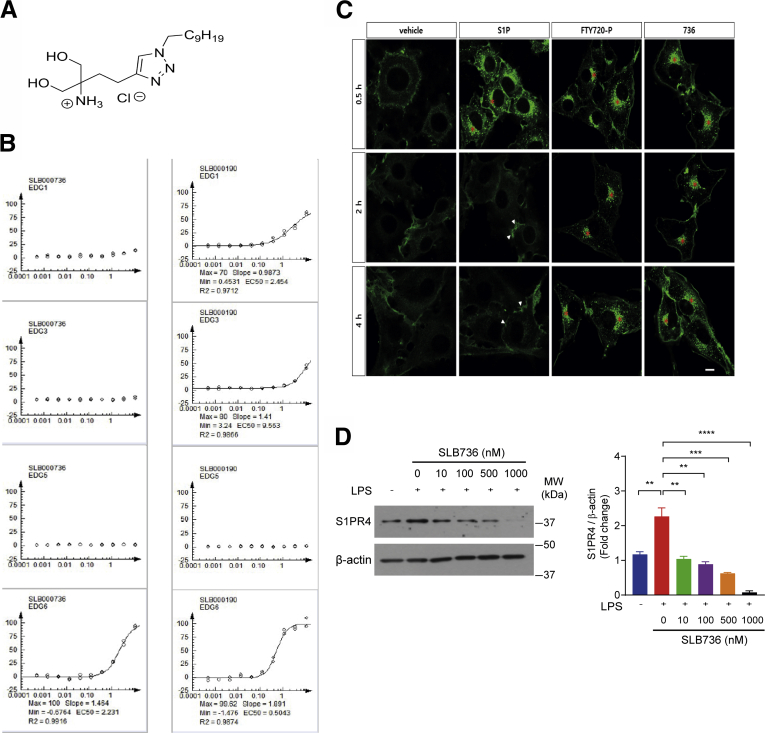
Figure 7.
SLB736 acts as a functional antagonist of S1PR4. (A) Structure of SLB736. (B) Isoform-specific S1PR activity of SLB736. β-arrestin PathHunter assay was performed in the clonal S1PR/HEK293 cell line in the presence of SLB736 (left) and FTY720-P (right). EDG 1 = S1PR1, EDG5 = S1PR2, EDG3 = S1PR3, EDG6 = S1PR4. (C) S1PR4 internalization and recycling were assessed in C6 glioma cells overexpressing EGFP-fused S1PR4. Cells were exposed to vehicle (0.1% BSA), S1P (100 nmol/L), FTY720-P (1 μmol/L), or SLB736 (1 μmol/L) for 0.5 hours and fixed. Cells exposed to reagents for 0.5 hours were washed and further incubated with vehicle in the presence of cyclohexamide for up to 4 hours. Asterisks or arrowheads indicate cytosolic locations or the cell surface. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Protein level of S1PR4 in hepatic macrophages. The S1PR4 protein was normalized to β-actin. Hepatic macrophages were pretreated with SLB736 at the indicated dose and then treated with 100 ng/mL of LPS for 24 hours (n = 4). All data are shown as means ± SEM. (D) Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni correction. ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. EC50, 50% Effective Concentration; Max, maximum; Min, minimum; MW, molecular weight.