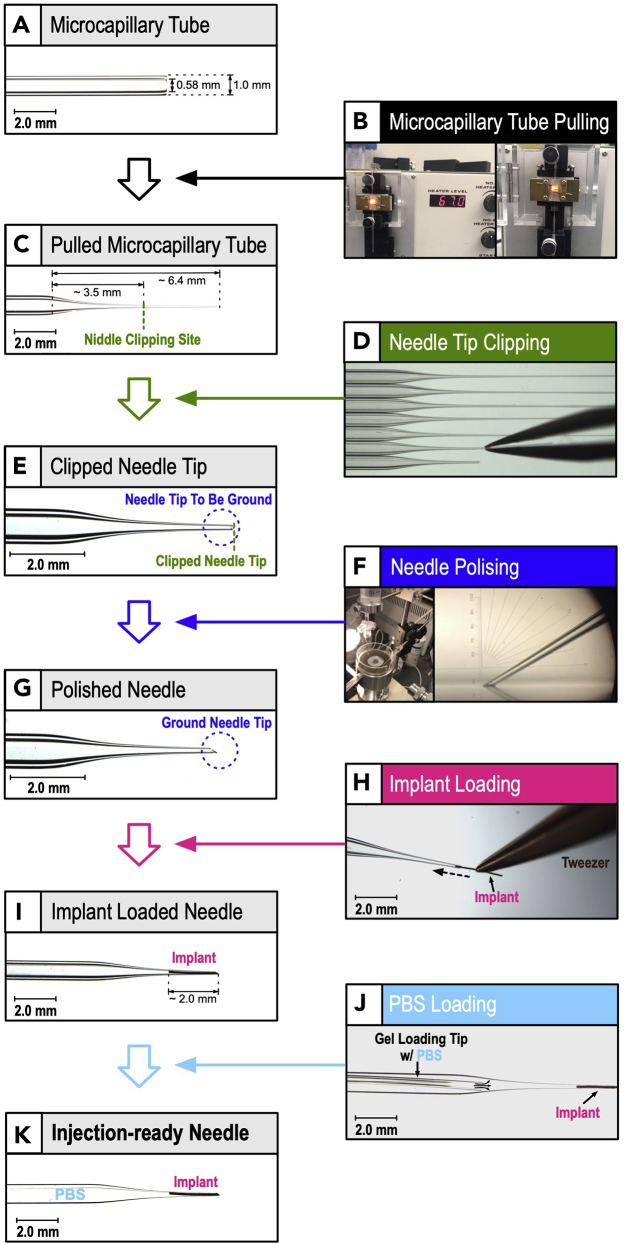
Figure 4.
Production schematics of implant-loaded intravitreal implant injection needle for mouse
(A) A borosilicate glass capillary, with inner and outer diameters of 0.58 and 1.00 mm respectively, was used.
(B) The microcapillary tube is pulled using a micropipette puller.
(C) General dimensions of pulled microcapillary tube.
(D and E) By using a clean forceps, the needle length is pulled to approximately 3–4 mm (needle clipping site in panel C) using clean forceps.
(F and G) The clipped needle tip is polished with the micropipette grinder to create a needle opening with a width of 80–100 μm and needle slant angle of 30°.
(H and I) 2 mm long implant is loaded to the needle using clean forceps.
(J and K) PBS is loaded to the needle using a pipette with gel loading tip.
(K) ODI needle ready for injection.