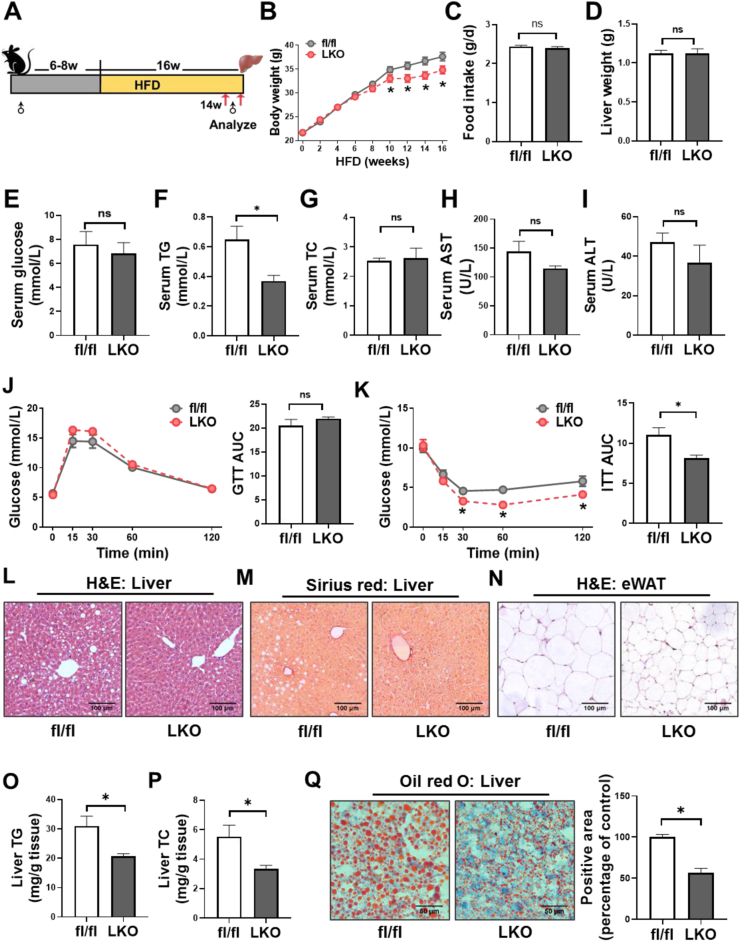
Figure 2.
CD36LKO mice were protected from HFD-induced hepatic steatosis. The hepatocyte-specific CD36 knockout (LKO) mice and control mice (fl/fl) were fed a HFD for 16 weeks (n = 12). A: Schematic experimental design to determine the effects of hepatocyte-specific CD36 on NAFLD. B-C: Body weight and daily food intake during the 16-week HFD condition were measured. D: Liver weight of 16-week-HFD-fed was measured. E–I: Overnight-fasted serum glucose levels (E), total triglycerides (TG) levels (F), total cholesterol (TC) levels (G), as well as ALT (H) and AST (I) levels were analyzed (n = 6). J–K: Glucose tolerance tests (GTTs, J) and insulin tolerance tests (ITTs, K) in HFD-fed mice. Quantification of the area under the curve (AUC) was shown in the right (n = 6). L–N: Representative images of hematoxylin & eosin (H&E)-stained livers (L), Sirius red-stained livers (M), and H&E-stained epididymal white adipose tissues (eWAT, N). Scale bar, 100 μm. O-P: Liver contents of TG and TC were determined (n = 6). Q: Representative images of Oil red O-stained livers. Quantification of Oil red O-stained area was shown in the right (n = 4; Scale bar, 100 μm). ∗P < 0.05 vs. fl/fl mice.