Figure 1. GudB interacts with GltAB in glutamate poor growth conditions.
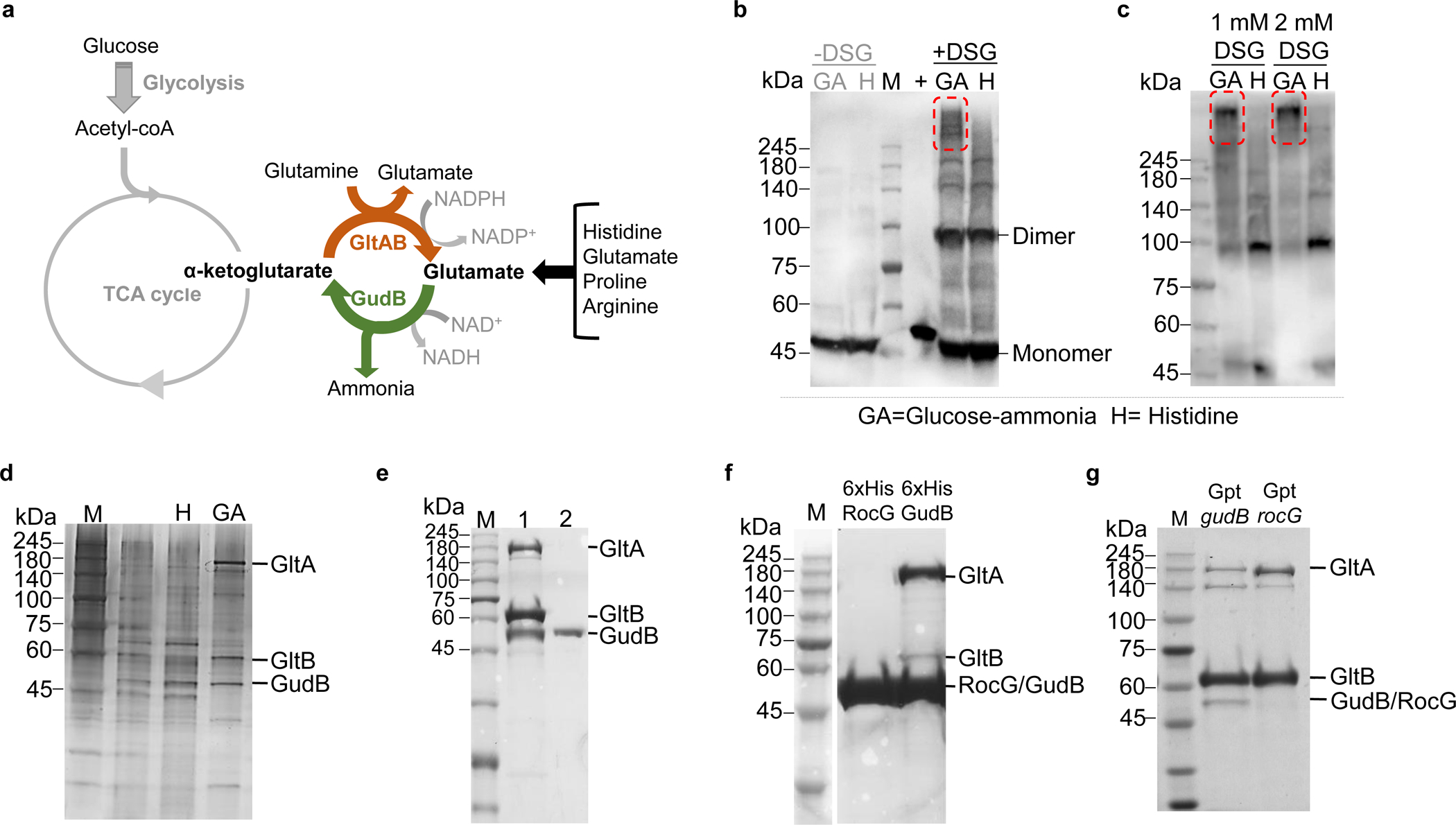
a) Key reactions involved in glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. Amino acids like proline, arginine, and histidine when provided as the sole C/N source are catabolized via glutamate. In contrast, growth on glucose as C source demands glutamate synthesis (via AKG). b) Western blot using anti-GudB antibodies indicating similar expression levels of GudB in B. subtilis cells grown in glucose-ammonia (GA) and Histidine (H) (-DSG). Upon treating with a chemical crosslinker (DSG, 0.5 mM), high molecular weight species that include GudB can be seen in cells grown on glucose-ammonia (GA, highlighted in red frame) but not on histidine (H). Recombinant GudB served as a positive control (+). c) The high molecular weight species of GudB are clearly seen in Western analysis of lysates from cells grown on glucose-ammonia (as in C) yet treated with higher concentration of DSG (1mM/2mM). d) Immunoprecipitation of GudB indicated co-elution of GltA and GltB in glucose-ammonia but not in histidine. The eluates from the pulldown was subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained with silver nitrate. e) SDS-PAGE showing co-elution of GudB and GltA upon purification of Strep-GltB from B. subtilis cells grown in glucose-ammonia (Lane 1; Lane 2 shows purified recombinant Strep tagged-GudB). f) Co-purification of GltA and GltB upon pulldown of His-tagged GudB but RocG. g) GudB but not RocG co-eluted upon pulldown of Strep-GltB from strains expressing either GudB or RocG from the constitutive gudB promoter (Gpt). Images b-g correspond to one replicate and are representative at least three independent experiments.
