Figure 3.
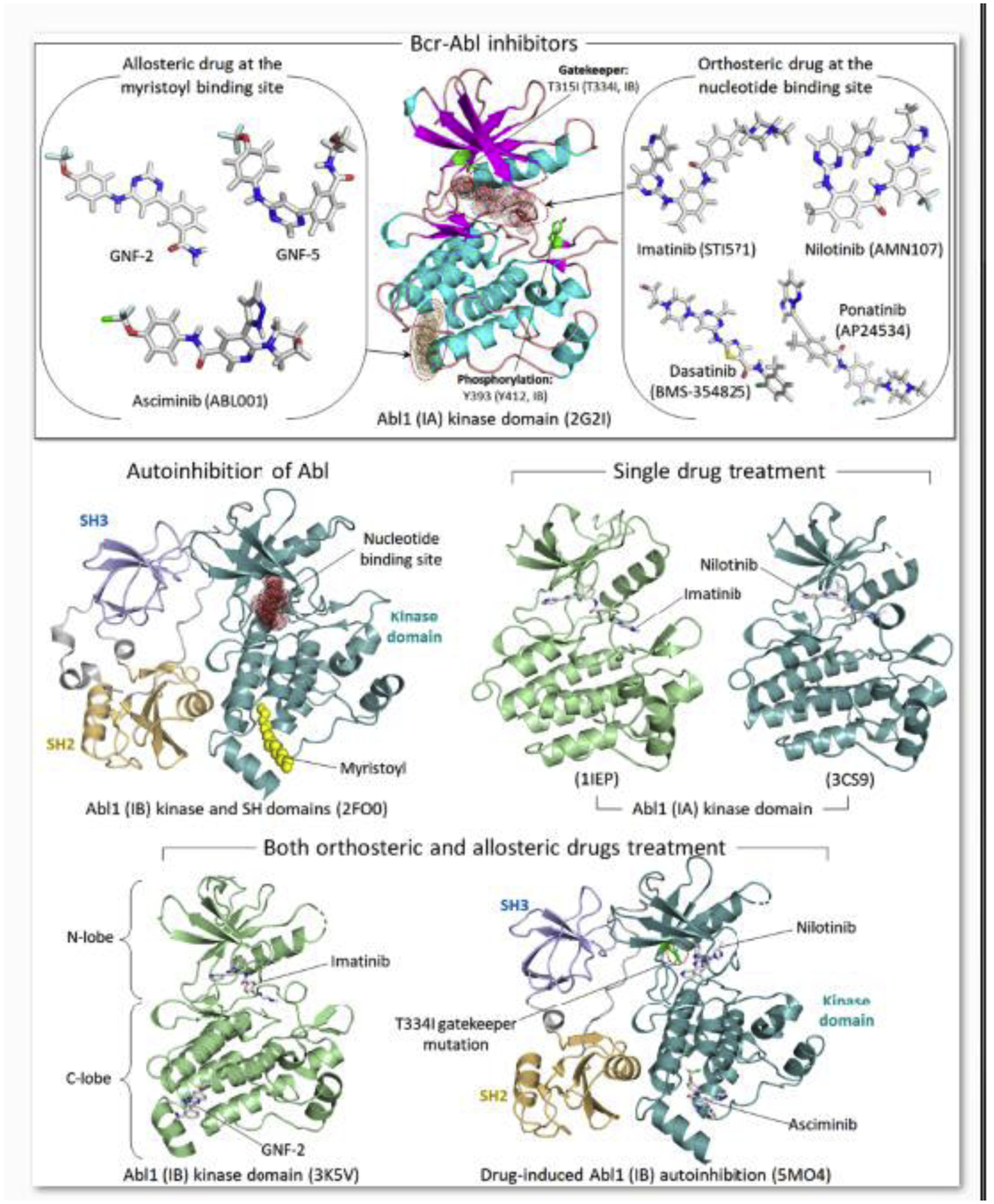
Inhibitors for Bcr-Abl fusion tyrosine kinase. Molecular structures of the drugs bound to the kinase domain of Abl (upper panel). Orthosteric ATP-competitive drugs, such as imatinib (STI571), nilotinib (AMN107), dasatinib (BMS-354825), and ponatinib (AP24534), can inhibit oncogenic Bcr-Abl kinase activity. However, drug resistance mutations in ATP-binding site, such as gatekeeper mutation T315I (Abl1 isoform IA; T334I for Abl1 isoform IB), or the activation loop can change conformation of the active site, preventing the orthosteric drugs from the oncogenic inhibition. Allosteric drugs bound to the myristate pocket, such as GNF-2, GNF-5 and asciminib (ABL001), can re-sensitize the orthosteric drugs, overcoming the drug resistant. Drug structures were obtained from PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), a public chemical database at the National Library of Medicine (NLM) (Kim et al., 2021). Examples shown for the crystal structures of Abl1 autoinhibition, drug-bound kinase domains, and drug-induced Abl1 autoinhibition (lower panels).
