Fig 3.
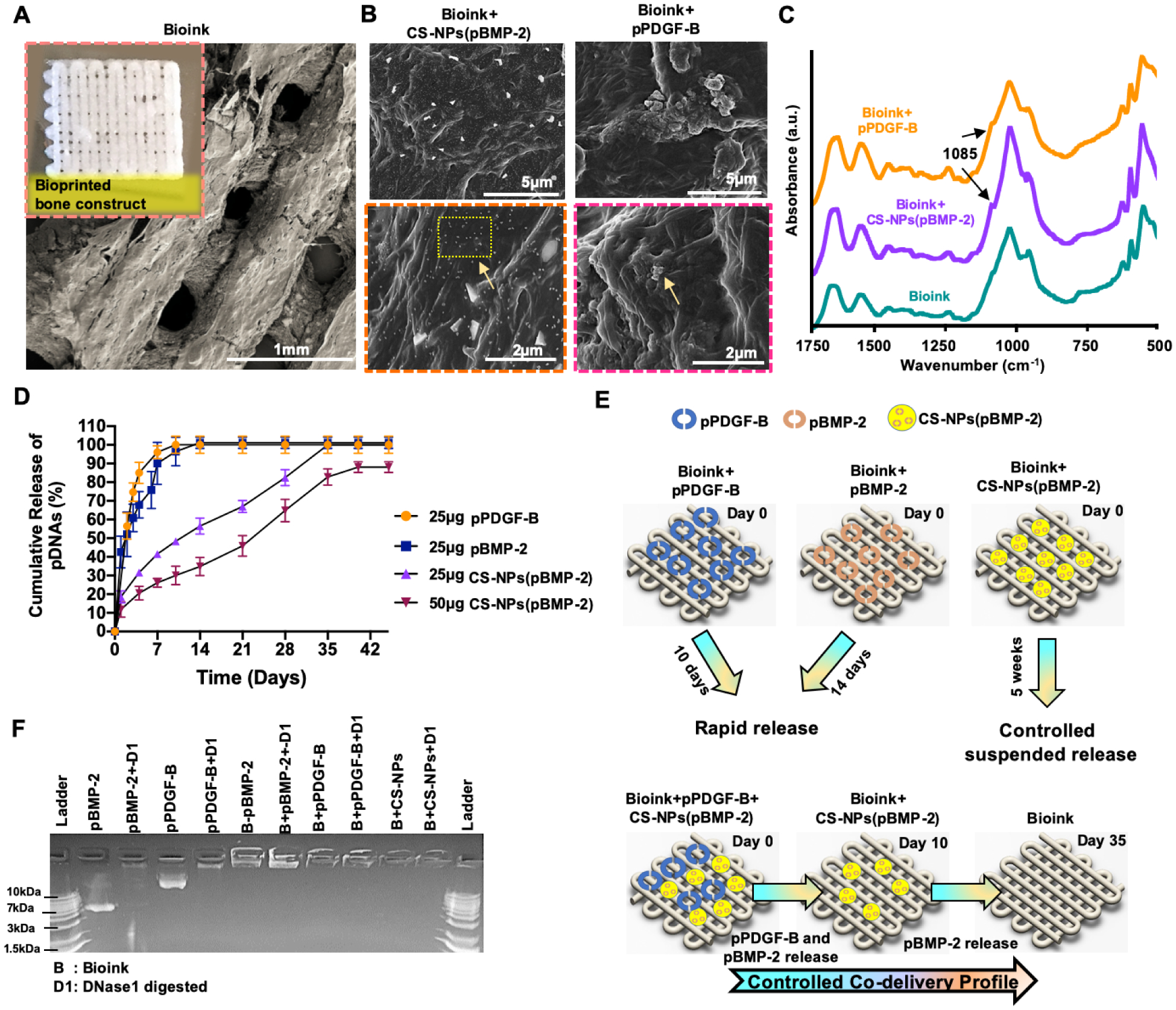
(A) 3D Bioprinted bone construct with well-defined porous architecture and its morphological display under SEM. (B) SEM images of encapsulated CS-NPs(pBMP-2) and (pPDGF-B). (C) ATR-FTIR spectra of the bioink, bioink+CS-NPs(pBMP-2) and bioink+pPDGFB. (D) In-vitro cumulative pDNA release profiles from 3D bioprinted constructs. (E) The release strategy of pDNAs from 3D bioprinted construct. (F) The agarose gel retardation assay demonstrating the stability of NPs and pDNAs in 3D bioprinted constructs. Data were presented as mean ± s.dev (n=3).
