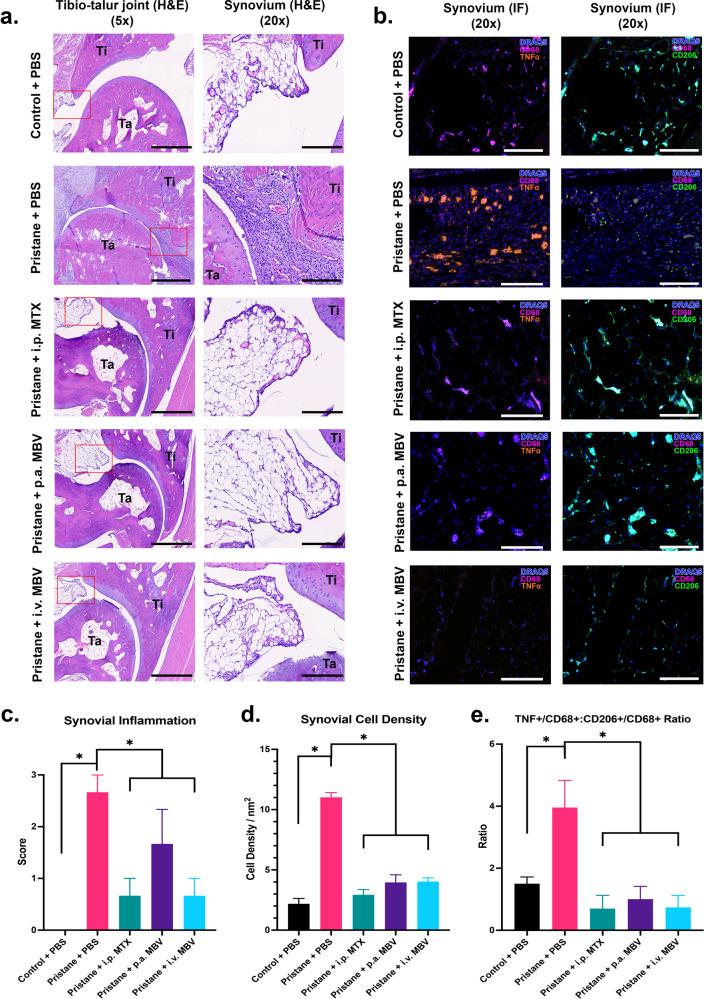
Fig. 4. MBV reduce synovial inflammation and decrease the ratio of pro-inflammatory M1-like synovial macrophages to anti-inflammatory M2-like synovial macrophages.
a Representative ×5 H&E images of the tibiotalar (tibia = Ti, talus = Ta) joint and ×20 H&E images of the adjacent synovium. Scale bar for ×5 images = 1000 µm. Scale bar for ×20 images = 200 µm. b ×20 immunofluorescent images of the synovium stained for M1-like synovial macrophages (DRAQ5+/CD68+/TNF-α+) in the left column and M2-like synovial macrophages (DRAQ5+/CD68+/CD206+) in the right column. Scale bar = 200 µm. c I.p. MTX, p.a. MBV, and i.v. MBV decrease overall synovial inflammation compared to the Pristane + PBS group (p < 0.05). d I.p. MTX, p.a. MBV, and i.v. MBV decrease synovial cellular density compared to the Pristane + PBS group (p < 0.05). e Compared to Control + PBS, pristane + PBS significantly increases the ratio of M1-like macrophages (TNF-α+/CD68+) compared to M2-like macrophages (CD206+/CD68+) (p < 0.05). All three treatment groups (i.p. MTX, p.a. MBV, and i.v. MBV) significantly reduce the ratio of M1-like:M2-like macrophages in the synovial tissue (p < 0.05) All values in panels c–e represent mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3).