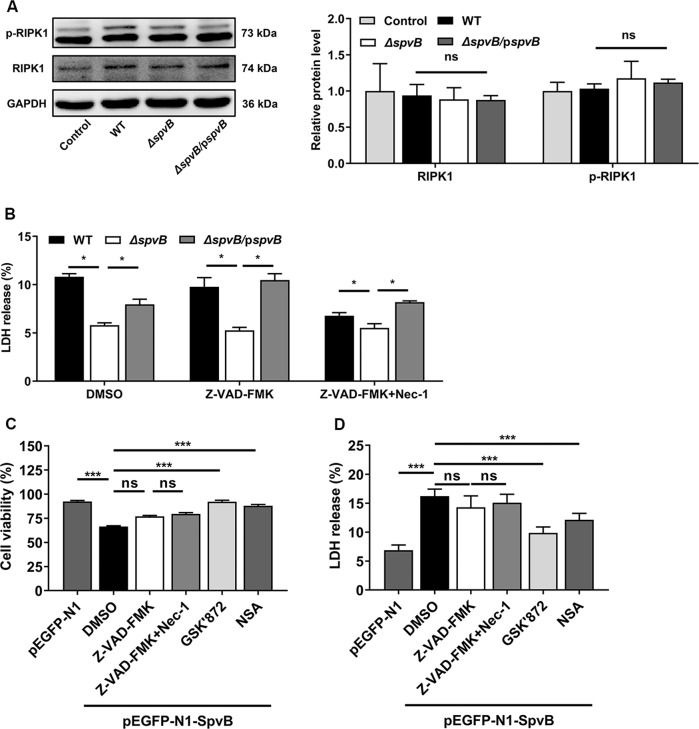
Fig. 3. SpvB promotes IECs necroptosis in a manner independent of RIPK1.
A Caco-2 cells were infected with WT, ΔspvB, or ΔspvB/pspvB S. Typhimurium strain (MOI of 100) and incubated for 4 h. Western blot analysis of the expression of RIPK1 and p-RIPK1. B Caco-2 cells were treated with either vehicle (DMSO), 20 µM Z-VAD-FMK with or without 10 µM necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) for 1 h. The cells were then infected with the WT, ΔspvB, or ΔspvB/pspvB S. Typhimurium strain (MOI of 100) and incubated for 24 h. Aliquots of cellular supernatants were subjected to LDH release assay. C, D Caco-2 cells were transiently transfected with pEGFP-N1 or pEGFP-N1-SpvB for 24 h. Cells transfected with pEGFP-N1-SpvB were pretreated with either vehicle (DMSO), 20 µM Z-VAD-FMK with or without 10 µM Nec-1, 1 µM GSK’872, or 1 µM NSA for 1 h. C Cells were subjected to cell viability assay. D Aliquots of cellular supernatants were subjected to LDH release assay. Data were analyzed with IBM SPSS Statistics 19 and presented as the mean ± SEM using Student’s t-test and ANOVA with S-N-K correction. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001; ns not significant.