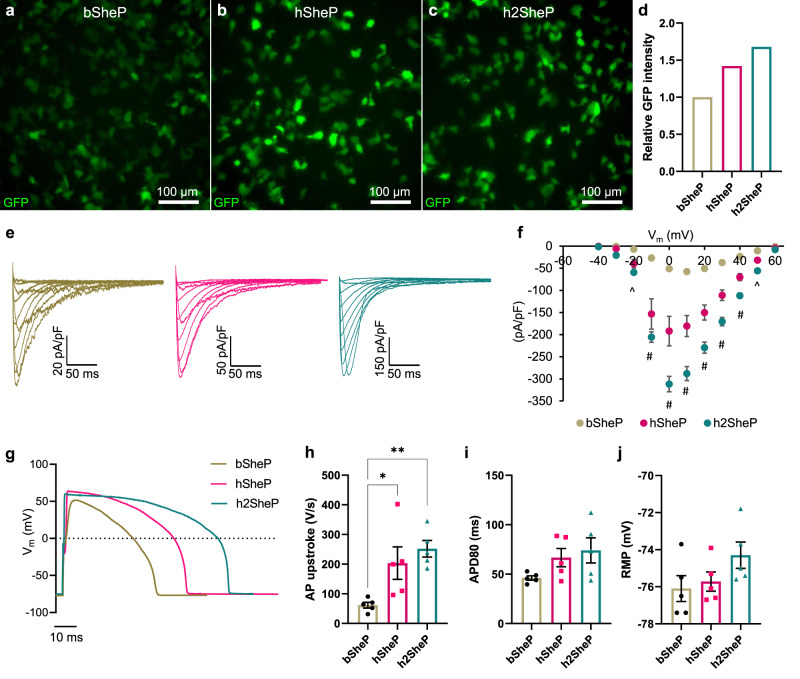
Fig. 1. Human codon optimization of BacNav gene improves expression of functional channels.
a–d Representative images of HEK293 cells transduced with bicistronic lentiviruses in which GFP gene was linked via T2A peptide with non-optimized (bacterial) NavSheP D60A sequence (bSheP, a) or NavSheP D60A sequences codon-optimized using Genscript (hSheP, b) or ATUM (h2SheP, c) algorithms and corresponding quantification by flow cytometry (d). e, f Representative current traces (e) and corresponding quantifications of peak INa–V curves (f) recorded in bSheP, hSheP, or h2SheP-expressing HEK293 cells using whole-cell voltage clamp at 25 °C (n = 6). g–j Representative action potential (AP) traces (g) measured via current clamp in BacNav-transduced Kir2.1-expressing HEK293 cells and corresponding quantifications of maximum upstroke velocity (h, AP upstroke; n = 5), AP duration at 80% repolarization (i, APD80; n = 5), and resting membrane potential (j, RMP; n = 5), all recorded at 37 °C. #P < 0.05 among all three groups and ^P < 0.05 for h2SheP vs. bSheP in f, exact P-values for all groups are included in Source Data. *P = 0.0403, **P = 0.0073 vs. bSheP in h. Error bars indicate s.e.m; statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA in f and one-way ANOVA in h, followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test to calculate P-values. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.