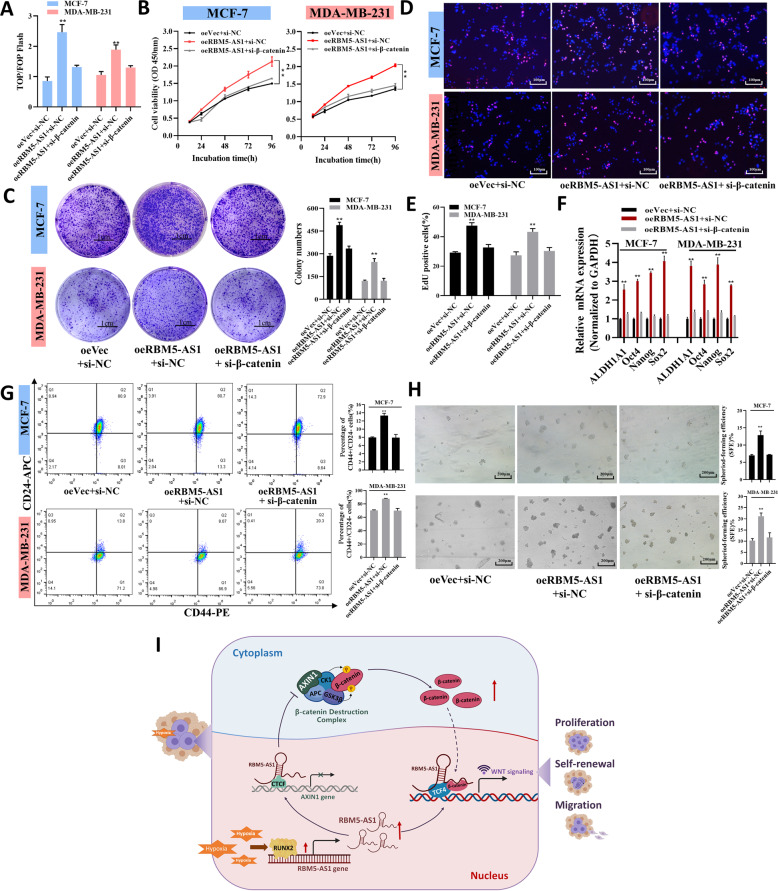
Fig. 8. Knockdown of β-catenin restores the proliferative and pro-stemness functions of RBM5-AS1 in breast cancer cells.
A The activation of the WNT/β-catenin signaling was detected using a TOP/FOP flash assay. Proliferative abilities of oeVec plus si-NC, oeRBM5-AS1 plus si-NC, or oeRBM5-AS1 plus si-β-catenin transfected MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were evaluated by CCK-8 assays (B), plate colony assays (C, Scale bar, 1 cm), and EdU assays (D and E, Scale bar, 100 μm). F mRNA levels of pluripotent transcription factors in oeVec plus si-NC, oeRBM5-AS1 plus si-NC, or oeRBM5-AS1 plus si-β-catenin transfected MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. G Proportion of CD44+CD24− cells in oeVec plus si-NC, oeRBM5-AS1 plus si-NC, or oeRBM5-AS1 plus si-β-catenin transfected MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. H Sphere-formation abilities of oeVec plus si-NC, oeRBM5-AS1 plus si-NC, or oeRBM5-AS1 plus si-β-catenin transfected MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Scale bar, 200 μm. I During breast tumorigenesis, RBM5-AS1 was upregulated by a hypoxia-induced transcriptional factor, RUNX2. RBM5-AS1 promoted proliferation, stemness, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells via activating the WNT/β-catenin pathway in two ways. On the one hand, RBM5-AS1 could prevent β-catenin degradation by repressing transcription of AXIN1, a core component of the β-catenin destruction complex, which in turn facilitated β-catenin nucleus accumulation. On the other hand, RBM5-AS1 could function as a scaffold for β-catenin-TCF4 complex, leading to transcriptional activation of WNT/β-catenin signaling. All data are shown as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by two-tailed Student’s t-test.