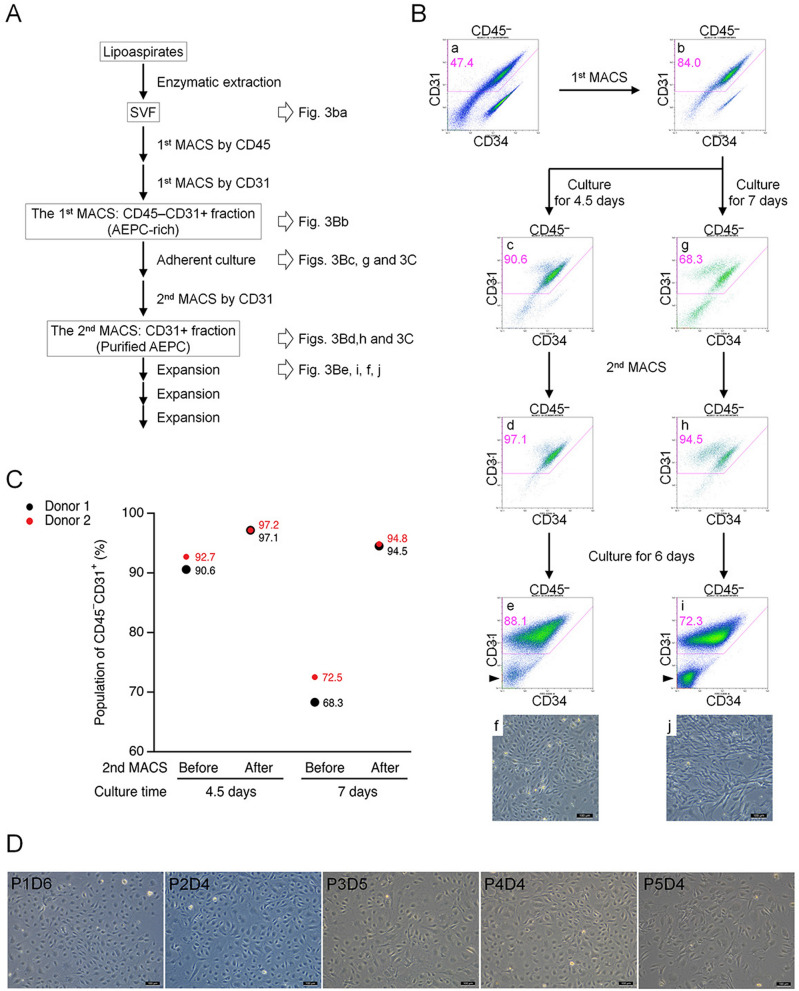
Figure 3.
Establishment of the AEPC purification. (A) Schematic view of the AEPC purification method from human lipoaspirates. AEPCs were purified from the SVF using two MACS sorting steps (CD45−CD31+ sorting and only CD31+ sorting) and adherent cultures. (B,C) Optimization of the timing for the second MACS sorting step for AEPC purification. Cells were dissociated from the cell culture surface with TrypLE Express Enzyme after either 4.5 or 7 days of culture and were subjected to MACS separation using CD31 microbeads. Cell surface markers (CD45, CD31, and CD34) were examined by flow cytometry. The percentage of CD45−CD31+ (AEPC) cells in CD45−CD31− (ASCs, isotype+ cells, other cells, and debris) cells is shown in magenta. ASCs drastically decreased CD34 expression in vitro, which could be observed in the CD45−CD31− population (arrowheads). Scale bars in microscopic photographs represent 100 µm. This experiment was performed twice, independently from 2 donors. (D) Morphologies of purified AEPCs over time. The photographs were taken using a phase-contrast microscope (Leica DM IL LED with a camera MC170HD; 100× magnification). P1D6 indicates the culture period at passage 1, after 6 days in culture. The experiment was performed twice, independently from 2 donors. Bars represent 100 µm.