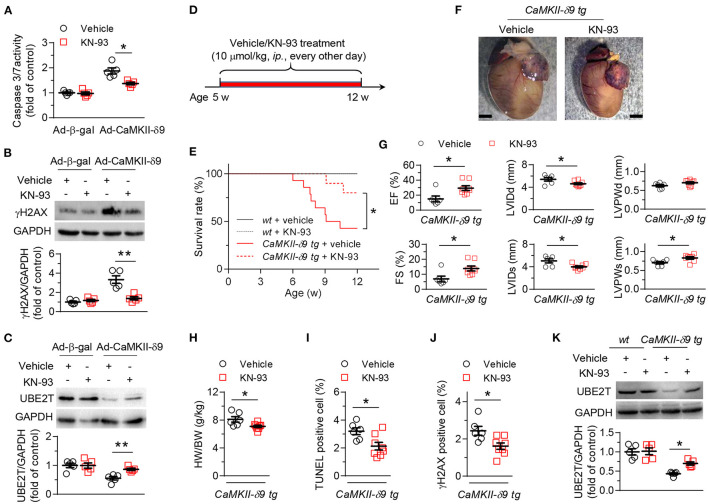
Figure 1.
KN-93 treatment prevents CaMKII-δ9-induced cardiomyopathy and heart failure. (A–C), Cell viability assayed by caspase 3/7 activity (A) and representative western blots and statistical data showing the levels of γH2AX (B) and UBE2T (C) in NRVMs infected with Ad-β-gal or Ad-CaMKII-δ9 with or without KN-93 treatment (5 μM) (n = 5). (D) Experimental protocol for in vivo KN-93 treatment in CaMKII-d9 tg mice. The mice were treated with KN-93 (10 μmol/kg, i.p.) every other day from 5 to 12 weeks of age. (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of wt and CaMKII-δ9 tg mice with or without KN-93 treatment (n = 8 for wt vehicle, n = 7 for wt KN-93, n = 14 for CaMKII-δ9 tg vehicle, n = 10 for CaMKII-δ9 tg KN-93). (F–J) Gross morphology of the hearts (F), statistical data of the left ventricle echocardiography (G), ratio of heart weight to body weight (H), and statistical data of TUNEL (I) and γH2AX (J) staining of the hearts from CaMKII-δ9 tg mice with or without KN-93 treatment. EF, ejection fraction; FS, fractional shortening; LVIDd and LVIDs, diastolic and systolic left ventricular internal diameter; LVPWd and LVPWs, diastolic and systolic left ventricular posterior wall thickness. Scale bar, 2 mm (n = 6 for vehicle, n = 8 for KN-93). (K) Representative western blots and statistical data showing the levels of UBE2T from the hearts of wt and CaMKII-δ9 tg mice with or without KN-93 treatment (n = 5). Data are mean ± S.E.M. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; two-way ANOVA (A–C,K), log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test, or Student's t-test (E,G–J).