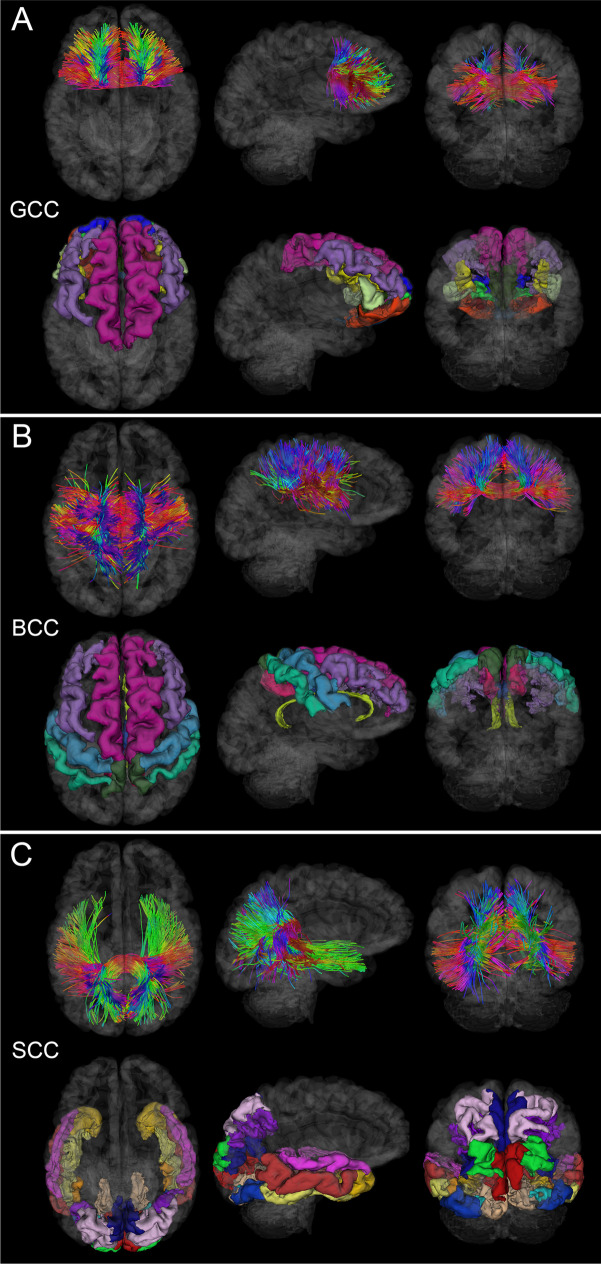
Fig. 2.
WM fasciculi whose mean FAs are significantly associated with age at injury either acutely or chronically. Fiber trajectories are encoded by colors (red: left–right; green: anterior–posterior; blue: inferior-superior). Axial, sagittal, and coronal views of WM structures are superimposed on a translucent model of the brain. The gyri and sulci connected by the corresponding WM pathways are also displayed. (A) GCC damage is associated with deficits of functions localized to the frontal and prefrontal cortex, including executive function and interhemispheric communication [24]. (B) BCC damage is frequently associated with somatomotor deficits [26]. (C) SCC injury can result in damage to circuits mediating visual, auditory, and somatosensory function, as well as multimodal sensory integration [25]