Fig. 4.
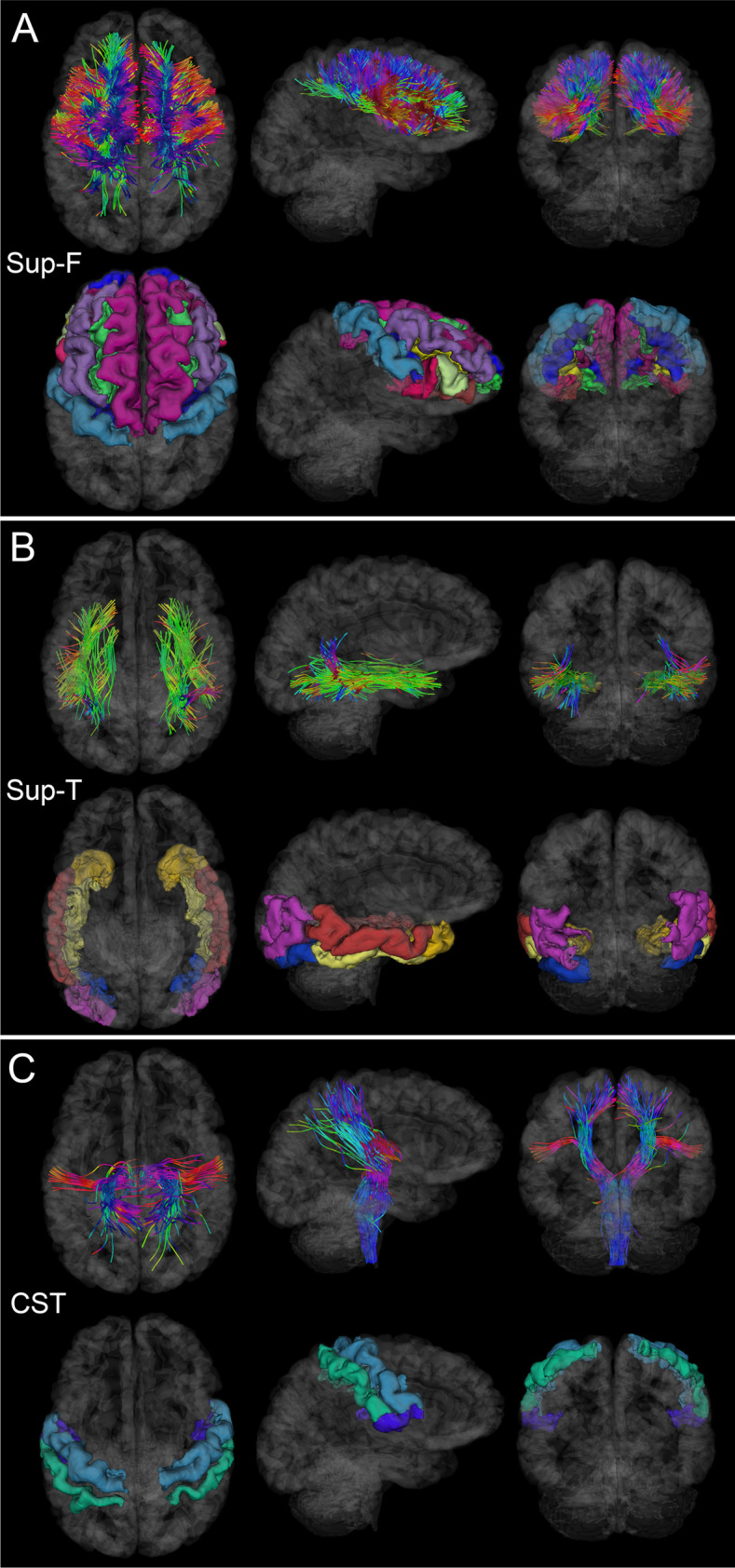
Like Fig. 2, for the Sup-F, Sup-T, and CST. (A) Sup-F fasciculi affected by injury can result in deficits of executive control [28]. (B) Sup-T fasciculi, when affected significantly by injury, may result in deficits pertaining to the recognition of faces and objects. (C) CST damage can affect the functions of the primary somatomotor cortex [40]
