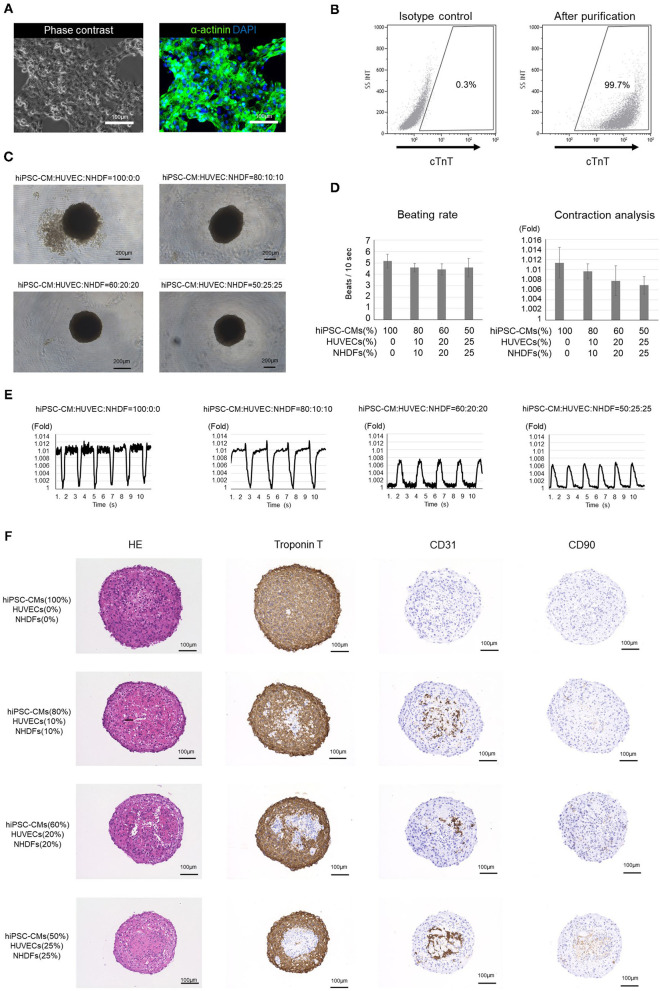
Figure 1.
Analysis of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) and cardiac organoids (COs). (A) Phase contrast image and immunostaining of purified hiPSC-CMs. (B) Flow cytometry of purified hiPSC-CMs. The proportion of cardiac troponin T-positive cells is >99%. (C) Outline structure of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiac organoids (hiPSC-COs). They are composed of hiPSC-CMs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), and normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDFs) seeded in four different ratios. The hiPSC-COs comprising 50% hiPSC-CMs, 25% HUVECs, and 25% NHDFs show a perfectly circular outline. (D) Beating rate and contraction analysis based on a fold change compared to the minimum area. The beating rate does not vary significantly among the four groups. The extent of contraction is maximum for the hiPSC-COs composed of 100% hiPSC-CMs. (E) Contraction of hiPSC-COs based on a fold change compared to the minimum area. The contraction is stronger in hiPSC-COs that are composed of a higher percentage of hiPSC-CMs. (F) Histological staining with hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemical staining for cardiac troponin T, CD31, and CD90.