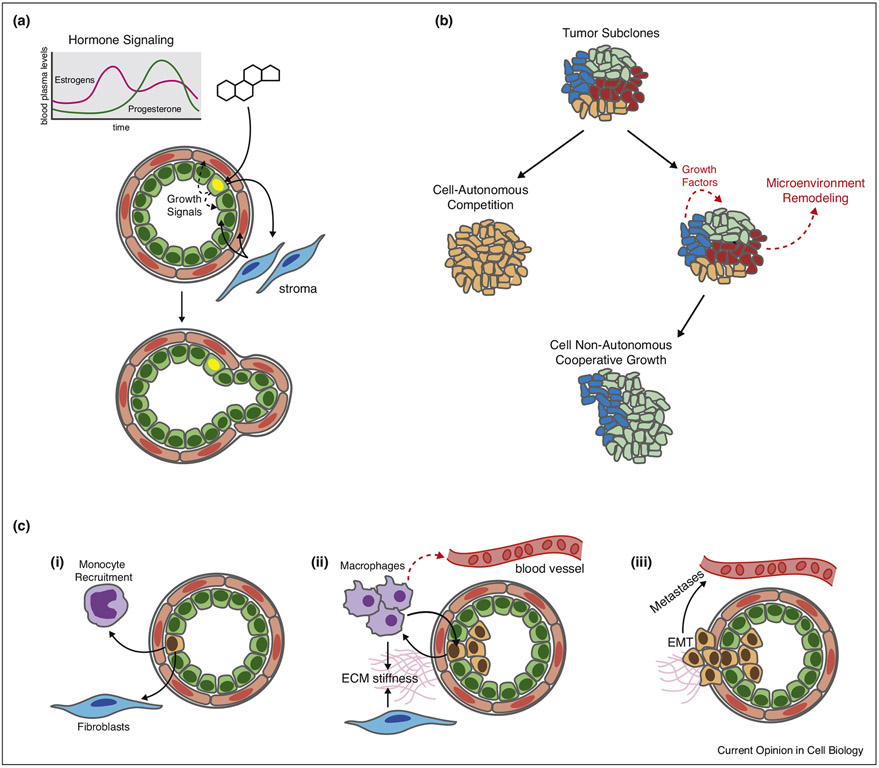
Figure 1.
Examples of non-cell autonomous growth. (a) Hormone signaling in the mammary gland. Hormone-sensing cells are restricted to the luminal epithelial lineage (green) and integrate cyclic hormonal signals, such as progesterone. These signals drive proliferation in neighboring cells via paracrine signaling both within the epithelium and through stromal–epithelial cross-talk. This key regulator of mammary gland growth is preserved but dysregulated in many breast cancers. (b) Tumor subclones can overgrow/compete (subclone sweep) with the neighbors or cooperate through secreted factors and physical remodeling of the microenvironment. (c) Monocytes and fibroblasts can be recruited to tumors by secretion of cytokines, where they mature into secretory macrophages and cancer-associated fibroblasts, which in turn can promote tumor proliferation through the secretion of additional cytokines and other forms of microenvironmental remodeling. This cross talk can enhance invasion, EMT, and ultimately, metastasis (Fig. 1a).