Figure 2. RASSF1A‐dependent upregulation of E3 ligase SNURF/RNF4 destabilizes HES1 through the formation of a RASSF1A‐RNF4‐HES1 complex.
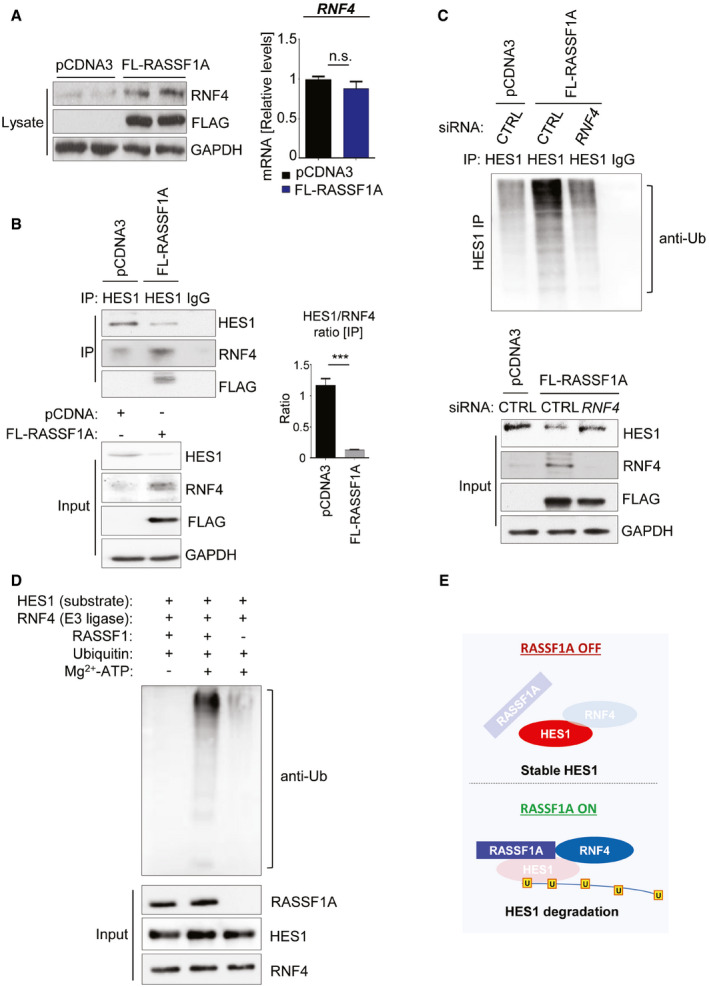
- U2OS cells were transfected with either pCDNA3 or FLAG‐RASSF1A. Cell extracts were collected and Western blotted with the indicated antibodies. qPCR from the same extracts demonstrated no significant differences in RNF4 mRNA levels.
- HES1 immunoprecipitation in U2OS cells treated with either pCDNA3 or FLAG‐RASSF1A and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Densitometry shows the HES1/RNF4 ratio is inversed upon RASSF1A induction. A RASSF1A‐RNF4 complex destabilizes HES1 through direct binding.
- In vivo ubiquitination assay in HES1 immunoprecipitates from U2OS cells transfected with either pCDNA3/siCTRL, FLAG‐RASSF1A/siCTRL, or FLAG‐RASSF1A/siRNF4 to assess Ub chain incorporation. Immunoprecipitates and Input lysates are probed with displayed antibodies. In the absence of RNF4, HES1 levels remain stable despite RASSF1A expression. See also Fig EV2B and C.
- In vitro ubiquitination assay using purified proteins for HES1, RASSF1A, and RNF4. RNF4 served as the E3 ligase of the reaction.
- Schematic illustrating the RASSF1A‐mediated regulation of HES1 stability via the E3 ligase RNF4.
Data information: ***P < 0.001 of Student’s t‐test; n.s., non‐significant. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Data shown are representative of three biological replicates (n = 3).
Source data are available online for this figure.
