Figure 4. Model.
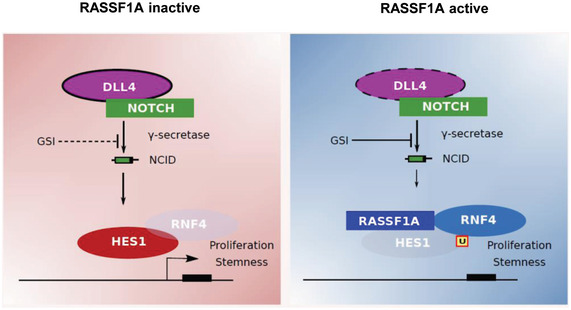
RASSF1A loss leads to HES1 stabilization in a Hippo pathway‐independent mechanism involving the E3 ligase SNURF/RNF4. In the absence of RASSF1A, HES1 levels remain unaffected by GSIs such as DBZ and DAPT. RASSF1A activation induces SNURF/RNF4‐mediated HES1 degradation via targeted HES1 ubiquitination. GSIs may further destabilize HES1 in the presence of RASSF1A. The RASSF1A status may constitute a robust biomarker of the effectiveness of Notch inhibitors in precision oncology.
