Figure 5.
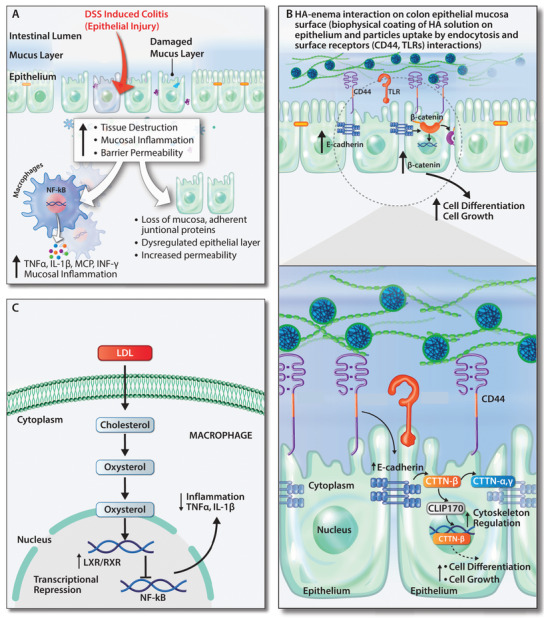
Possible mechanistic role of the HA‐enema suspension in the DSS induced colitis mucosal epithelium. A) External mucosal inflammation trigger (DSS solution) in the intestinal lumen causes the epithelium/mucosal damage. In downstream causes destruction of the tissue, inflammation of the colon epithelium, and an increase in the overall gut wall's permeability. B) Biphasic HA‐enema favorably provides mucoadhesive cementing protective barrier effect. The HA‐functionalized polymeric particles, HA solution both interact with cell surface receptors (including CD44, TLRs), upregulate the epithelial adherent junctional proteins E‐cadherin, β‐catenin which regulate the cytoskeleton, cell growth and repair on the dysregulated colitis wall. C) The LXR/RXR pathways were activated by HA‐enema via LDL uptake in macrophages and activate the LXR/RXR pathway, inhibiting the inflammation (NF‐kB) pathway leads to decreasing inflammation. The developed HA‐enema system serves as physical surface matrix barrier and protects from DSS external stimuli and might help in maintaining the gut barrier integrity in a DSS colitis mice model.
