Figure 4.
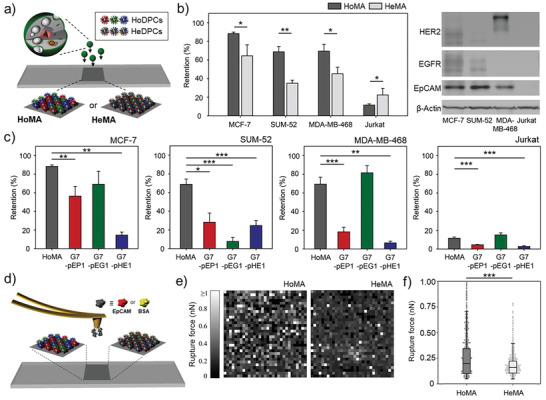
Two distinct hetero‐HMAs, HoMA (a heterogeneous mixture of homogeneous DPCs) and HeMA (a homogeneous mixture of heterogeneous DPCs), which display various peptides interacting with different types of proteins: a) A schematic illustration of HoMA and HeMA surfaces. b) The retention of surface‐bound MCF‐7, SUM‐52, MDA‐MB‐468, and Jurkat cells on HoMA and HeMA surfaces (left). Western blot analysis of EpCAM, HER2, and EGFR expression levels on the cell lines used in this study (right). c) The retention of surface‐bound MCF‐7, SUM‐52, MDA‐MB‐468, and Jurkat cells on HoMA compared to HMAs functionalized with a single type of peptides. d) A schematic illustration of atomic force microscopy (AFM) force mapping on HoMA and HeMA. e) AFM force mapping analysis using EpCAM‐immobilized probes to demonstrate the binding avidity of HoMA and HeMA against EpCAM protein. A 32 × 32 grid of retraction curves were obtained in the desired area of 10 × 10 µm2. f) Rupture forces based on AFM adhesion forces measured using EpCAM‐immobilized probes on HoMA and HeMA. Significance levels are indicated as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001, which are analyzed using Student's t test (cell retention) or the Mann–Whitney U test (AFM analysis).
