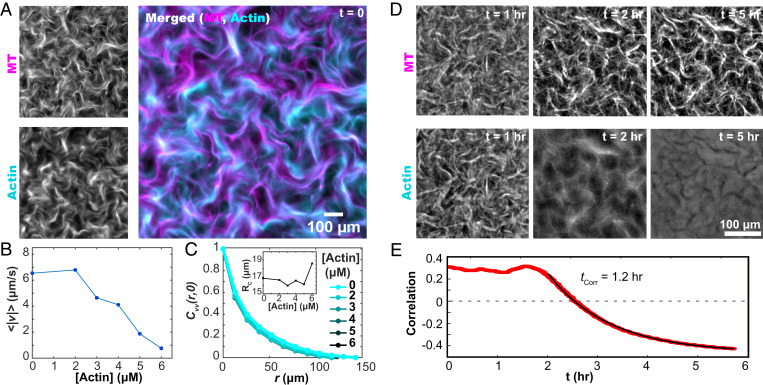
Fig. 2.
F-actin controls the dynamics of the extensile MT network. (A) Kinesin motors drive the reorganization of both F-actin and MT networks. (B) The mean speed of the autonomous flows decreases with increasing F-actin concentration. (C) The spatial velocity–velocity correlation function of the autonomous flows is independent of the F-actin concentration. (C, Inset) The correlation lengthscales, extracted from fits to exponential decay, are independent of F-actin concentration. (D) Upon cessation of motor-driven flow, F-actin relaxes away from its out-of-equilibrium configuration while the MT bundles remain fixed (Movie S3). (E) After motor-driven activity halts at 1.8 hours, the spatial correlation between the MT and F-actin concentration fields decreases as a function of time.