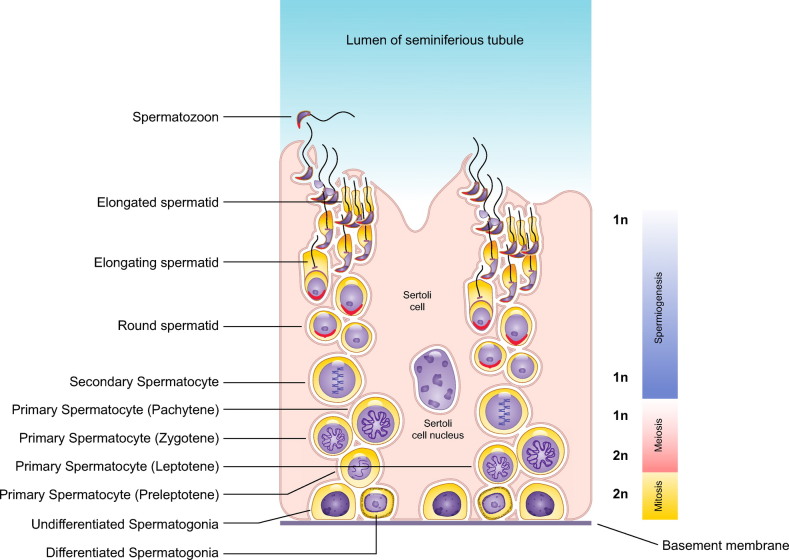
FIGURE 5.
Schematic representation of the mouse spermatogenic process. Spermatogenesis advances from the base to the lumen of the seminiferous tubule in a dynamic contact with Sertoli cells. Spermatogonia reside in the basal compartment and proliferate to primary spermatocytes (preleptotene, leptotene, zygotene, and pachytene). Secondary spermatocytes undergo second meiosis and became round spermatids. The sperm differentiation phase starts at this point with morphological and molecular transformations of round spermatids into elongating spermatids. Elongated spermatids are cells in the process of spermiation undergoing the final cellular transformations. In the last steps of spermiation, most of the cytoplasm will be removed and phagocytized by Sertoli cells to form fully developed spermatozoa.