Figure 9.
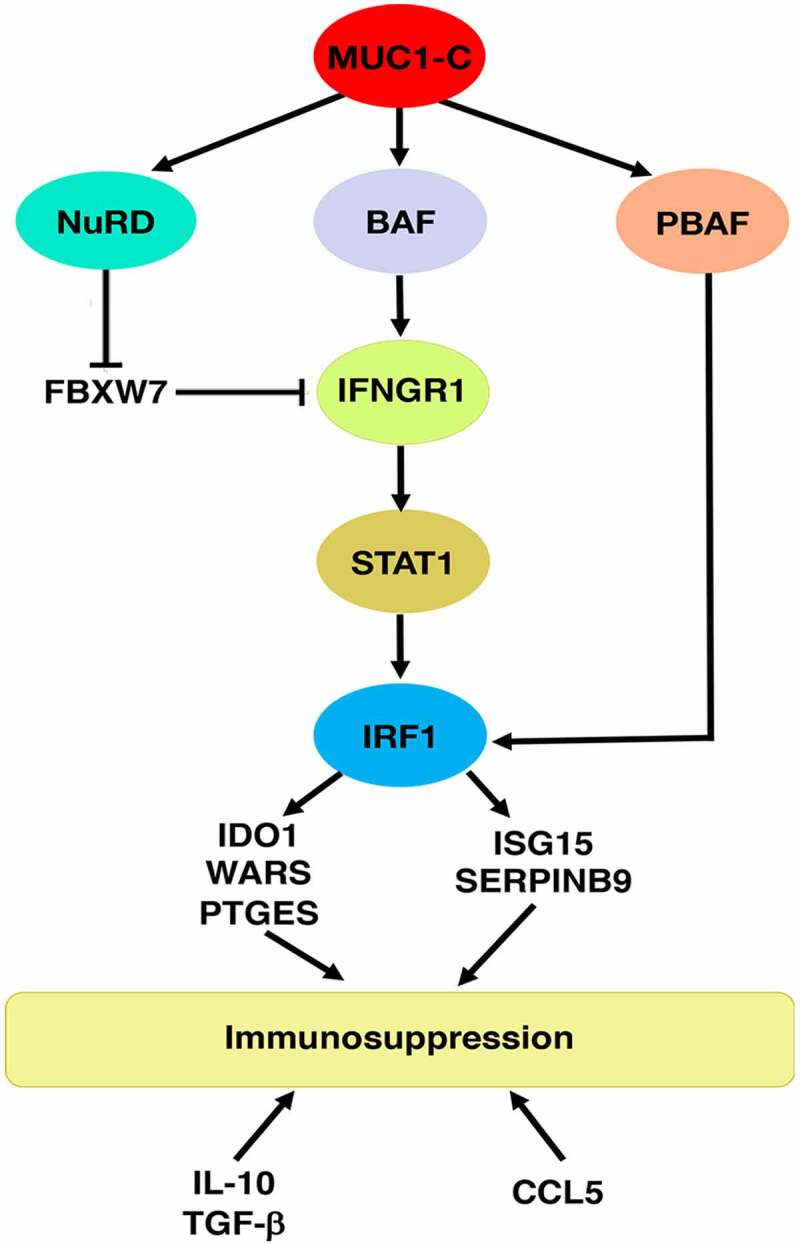
Schema depicting MUC1-C-induced chronic activation of the type II IFNG pathway, chromatin remodeling complexes and immunosuppression. MUC1-C drives expression of the BAF, NuRD and PBAF complexes. MUC1-C activates IFNGR1 by forming a complex with JUN and recruiting ARID1A/BAF to a dELS, which increases chromatin accessibility, H3K4 trimethylation and IFNGR1 expression. MUC1-C also stabilizes IFNGR1 by NuRD-mediated repression of FBXW7, an effector of IFNGR1 degradation. In turn, MUC1-C contributes to upregulation of STAT1, as well as IRF1, which interacts with PBRM1/PBAF in inducing expression of (i) IDO1, WARS and PTGES that metabolically suppress the immune TME, and (ii) the ISG15 and SERPINB9 inhibitors of T cell function. MUC1-C-high PC tumors also associate with increased expression of the immunosuppressive IL-10 and TGFB1 cytokines and the CCL5 chemokine. Consistent with these results, MUC1-C drives negative regulation and depletion of immune effectors in the PC TME.
