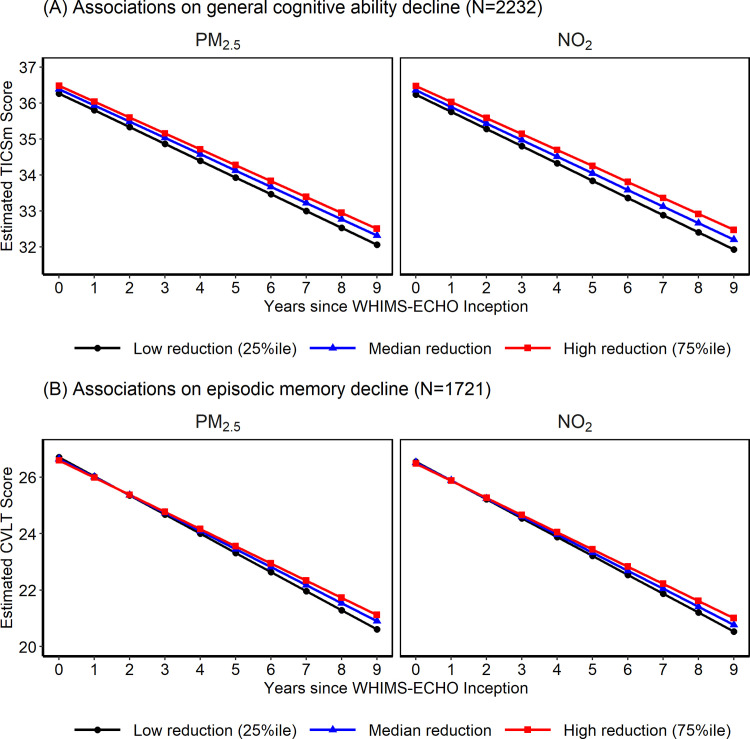
Fig 2. Estimated cognitive trajectory over time with different levels of AQ improvement in WHIMS-ECHO cohort.
(A) Associations on general cognitive ability decline (N = 2,232). (B) Associations on episodic memory decline (N = 1,721). Estimated TICSm score (panel A) or CVLT score (panel B) change over time for low (25th percentile), median, and high (75th percentile) level of AQ improvement in PM2.5 or NO2 in the WHIMS-ECHO cohort. The estimated TICSm scores or CVLT scores were calculated using parameter estimates derived from Model III of Table 3, which were adjusted for spatial random effect, WHIMS-ECHO enrollment year, age, follow-up year, age interaction with follow-up year, time-varying propensity scores, demographic variables (geographic region and race/ethnicity), socioeconomic factors (education, income, and employment status) and neighborhood characteristics, lifestyle factors (smoking, drinking, and physical activities), prior hormone use, hormone therapy assignment, cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia), depression, BMI, and CVD histories. AQ, air quality; BMI, body mass index; CVD, cardiovascular disease; CVLT, California Verbal Learning Test; NO2, nitrogen dioxide; PM2.5, fine particulate matter; TICSm, modified Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status; WHIMS-ECHO, Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study-Epidemiology of Cognitive Health Outcomes.