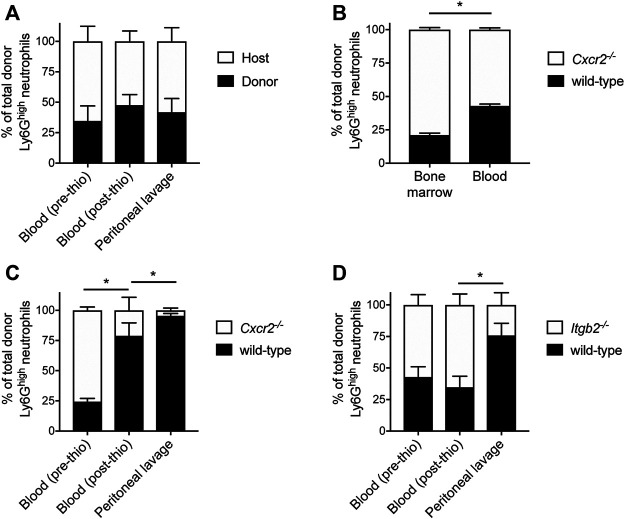
FIGURE 4.
Mechanisms underlying mobilization and recruitment of donor-derived neutrophils. Wild-type HoxB8-conditional progenitors, alone (A) or mixed with CXCR2-deficient (B,C) or β2 integrin-deficient HoxB8-conditional progenitors (D), were transplanted into CD45.1 recipient mice. (A, C,D) Mice were subjected to sterile peritonitis induced by thioglycollate. Blood samples (before and after thioglycollate injection) and peritoneal lavage were analyzed for the frequency of donor-derived wild-type and gene knockout neutrophils, as indicated. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. Statistical comparisons were made only between adjacent compartments/time points. *p < 0.05. (B) In mice not subjected to any inflammatory stimulus, bone marrow and blood samples were collected at day 8 post-transplant and analyzed for the frequency of donor-derived wild-type and CXCR2-deficient neutrophils. Data were analyzed using a paired Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05.