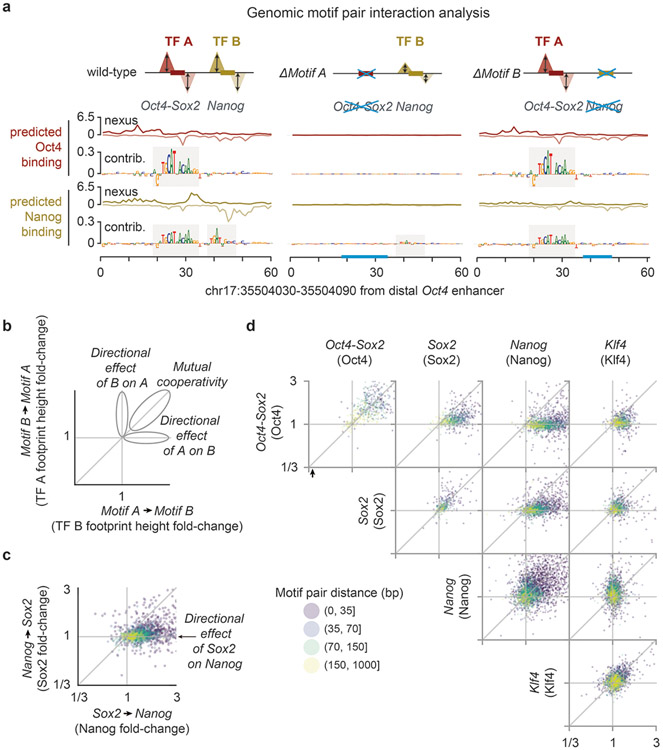
Extended Data Fig. 6. Additional genomic in-silico interaction analyses confirm the directional effects.
a) Example genomic in-silico mutagenesis analysis at the distal Oct4 enhancer. Predicted ChIP-nexus profiles and the contribution scores greatly decrease at both motifs (Oct4-Sox2 and Nanog) when erasing the Oct4-Sox2 motif (through random sequence insertion). By contrast, when the Nanog motif is erased (right), the predicted profile and the contribution scores of Oct4-Sox2 motif remain intact. b) Such directional effect of motifs can be quantified by the corrected binding fold change (Supplementary Fig. 10a) for all motif pairs in the genome and visualized as a scatterplot. c) Example scatterplot for the interaction between Sox2 and Nanog. Sox2 shows a positive directional effect on Nanog most profound for short motif distances (<35 bp). d) Predicted binding fold changes for all motif pairs in genomic sequences.