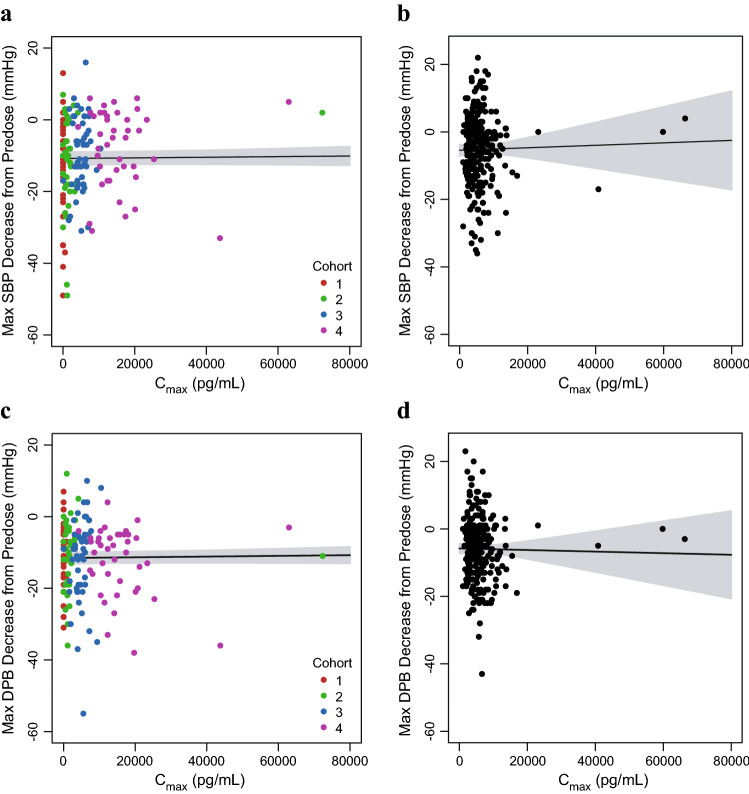
Fig. 9.
Visit-matched vosoritide Cmax in plasma and maximum decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressures in the phase II and III studies. a Points represent the individual patient maximum decrease in SBP and individual plasma vosoritide Cmax at each visit during the initial 6 months of the phase II study, color-coded by study cohort (C1: Cohort 1, 2.5 µg/kg; C2: Cohort 2, 7.5 µg/kg; C3: Cohort 3, 15 µg/kg; C4: Cohort 4, 30 µg/kg). One patient had a high Cmax (8.39 × 105 pg/mL) relative to other patients, but a within-range maximum decrease in SBP (−7 mmHg). This patient was included in the fit through the data but was not included in this figure. b Points represent the individual patient maximum decrease in SBP and individual plasma vosoritide Cmax at each visit during the phase III study. c Points represent the individual patient maximum decrease in DBP and individual plasma vosoritide Cmax at each visit during the initial 6 months of the phase II study, color-coded by study cohort (C1: Cohort 1, 2.5 µg/kg; C2: Cohort 2, 7.5 µg/kg; C3: Cohort 3, 15 µg/kg; C4: Cohort 4, 30 µg/kg). One patient had a high Cmax (8.39 × 105 pg/mL) relative to other patients, but a within-range maximum decrease in DBP (−2 mmHg). This patient was included in the fit through the data but was not included in this figure. d Points represent the individual patient maximum decrease in DBP and individual plasma vosoritide Cmax at each visit during the phase III study. Solid lines represent the linear fits through the data and the shaded regions represent the 95% confidence interval. The respective analyses using the individual patient AUC are similar and are shown in Fig. S9 in the ESM. Cmax maximum observed plasma concentration, SBP systolic blood pressure, DBP diastolic blood pressure, mmHg millimeter of mercury, ESM electronic supplementary material