Figure 5.
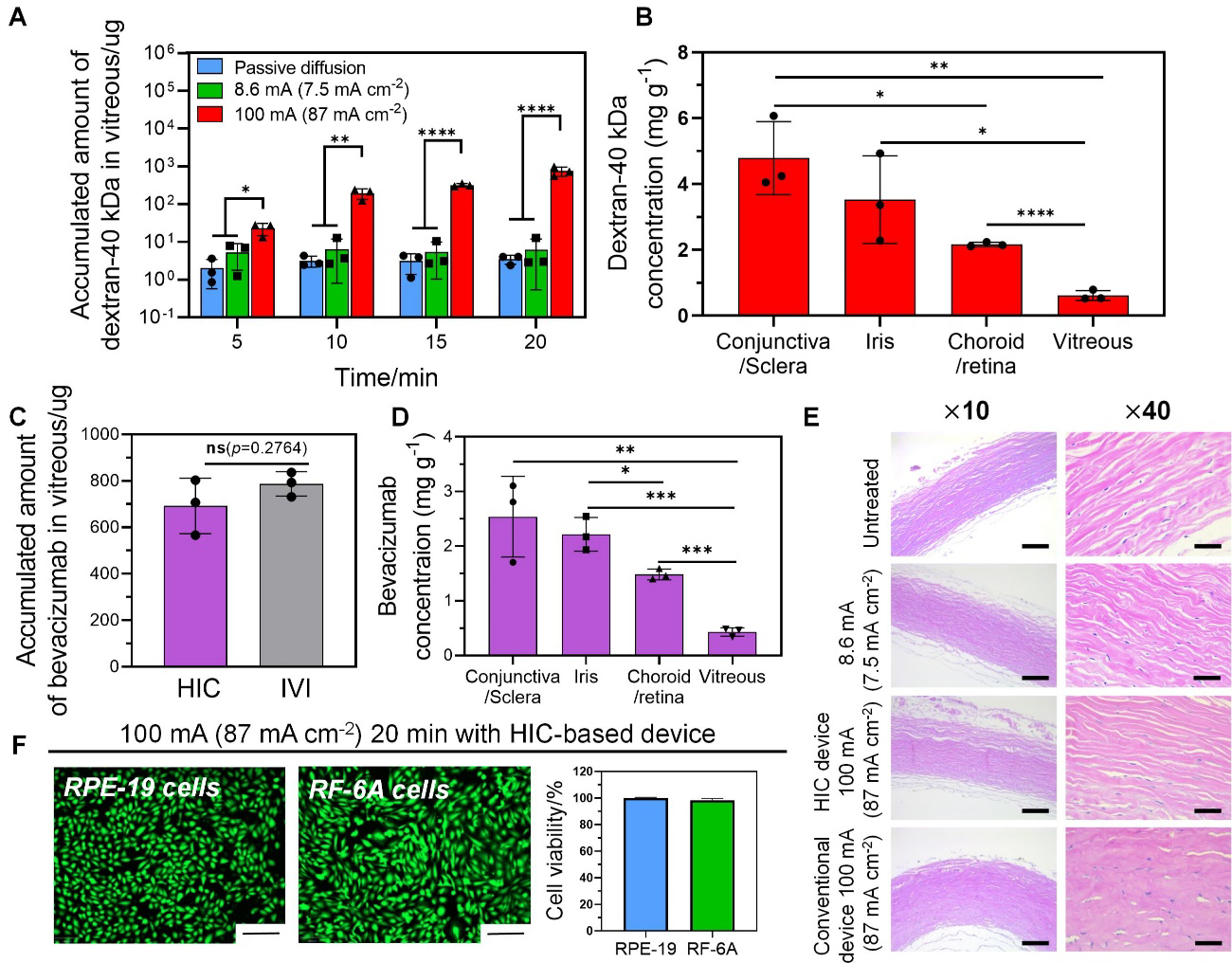
Drug delivery of dextran-40 kDa and bevacizumab to the posterior segments of excised rabbit eyeballs by high-intensity iontophoresis applied by our HIC-based device. (A) Accumulated amount of dextran-40 kDa in vitreous after iontophoresis (100 mA (87 mA cm−2)) for 5 min, 10 min, 15 min, and 20 min, respectively. (B) Accumulated concentration of dextran in various ocular tissue segments after high-intensity iontophoresis at 100 mA (87 mA cm−2) for 20 min. (C) Accumulated amount of bevacizumab in the vitreous after high-intensity iontophoresis (100 mA (87 mA cm−2), 20 min), and an intravitreal injection of bevacizumab (1.25 mg 50 μL−1). (D) Accumulated concentration of bevacizumab in various ocular tissue segments after high-intensity iontophoresis at 100 mA (87 mA cm−2) for 20 min. (E) Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining images for histological analysis of the sclera after iontophoresis under different test conditions (no treatment, low-intensity iontophoresis at 10 mA (7.5 mA cm−2) for 20 min applied by our HIC-based device, high-intensity iontophoresis at 100 mA (87 mA cm−2) for 20 min applied by our HIC-based device and a conventional device) (scale bars: ×10–100μm, ×40–25 μm). (F) The viability of retinal pigmented epithelium cell (RPE-19) and choroid/retina endothelial cell (RF/6A) (normalized to untreated control) after treated by 100 mA (87 mA cm−2) ion current for 20 min applied by our HIC-based device (scale bar: 200 μm).
