Figure 7. METTL7B-interacting proteins are enriched in the endoplasmic reticulum and lipid droplets.
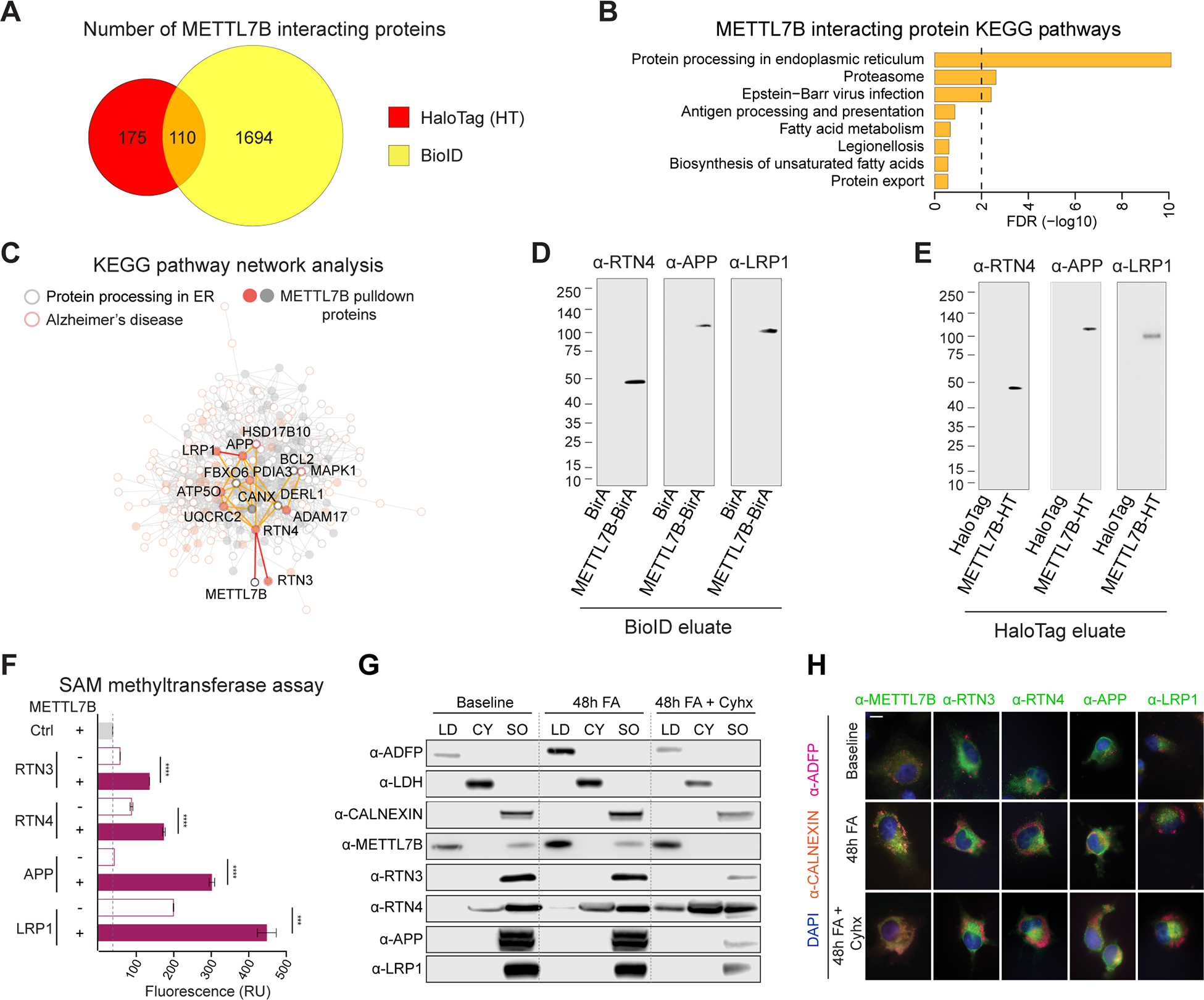
A, Venn diagram of high-confidence METTL7B interacting proteins revealed by HaloTag and BioID. B, KEGG enrichment of METTL7B interacting proteins from the intersection of HaloTag and BioID. C, Interaction network with proteins in KEGG Protein Processing in the ER pathway (grey) and Alzheimer’s disease pathway (orange). METTL7B interactors are shown as filled circles. D-E, Immunoblot confirmation of top interacting candidates. The molecular weight of the RTN4-immunoreactive band is consistent with a known proteolytic fragment of RTN4A or RTN4B (Kim et al., 2003; Sekine et al., 2020). F, SAM methyltransferase activity assay showing an increased reactivity in the presence of METTL7B. P-values calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, N=3. G-H, Immunoanalysis of METTL7B translocation. Increased fatty acid (FA) load leads to a shift of METTL7B from ER to lipid droplets (LDs), while high confidence interactors remain unaffected. Blocking translation of new proteins with cycloheximide (Cyhx) suggests a complete shift of METTL7B. Scale bar = 10 μm. CY = cytosol; SO = sedimented organelle (containing the ER). All data are mean ± SEM. ****P< 0.0001, ***P< 0.001. See also Figures S6, S7, and Tables S4.
