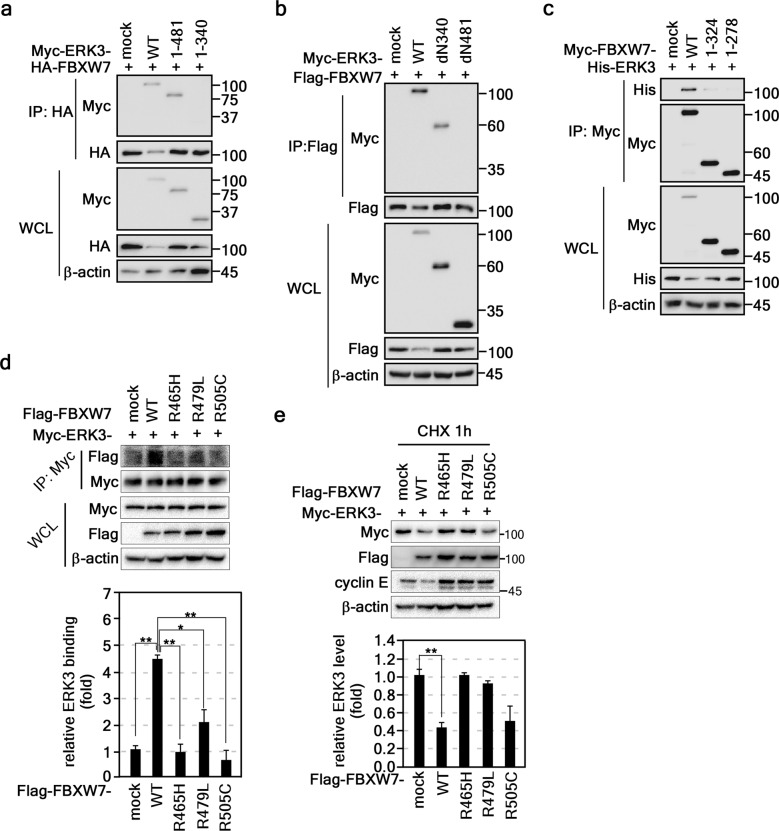
Fig. 3. The C34D of ERK3 interacted with the WD40 domain of FBXW7.
a Identification of ERK3 domains that interact with FBXW7. The ERK3 domains interacting with FBXW7 were determined by IP (HEK293T cell lysate, 300 μg cell lysate/lane) and Western blotting. b Involvement of the ERK3 C34D in its interaction with FBXW7. The ERK3 C34D was determined to interact with FBXW7 by IP (HEK293T cell lysate, 300 μg)/Western blotting. c Determination of FBXW7 domains that interact with ERK3. The FBXW7 interaction domains interacting with ERK3 were determined by IP (HEK293T cell lysate, 300 μg) and Western blotting. d Upper panels, Confirmation that the WD40 domain interacts with ERK3. The interactions of FBXW7 proteins containing each mutation in the WD40 domain and ERK3 were determined by IP and Western blotting (MG132; 10 μM, 4 h). Graphs, Immunoprecipitated FBXW7 protein levels were normalized to the levels of immunoprecipitated Myc-ERK3. e Upper panels, ERK3 protein levels were sustained in FBXW7 mutants. The ERK3 protein levels in HEK293T cells transiently expressing ERK3 and each FBXW7 mutation as indicated were determined by Western blotting (CHX; 10 μg/ml, 1 h). Graphs, The Myc-ERK3 band intensities were normalized to the β-actin intensity. a–e β-Actin was used as the internal control to ensure equal protein loading. WCL, whole-cell lysate.